I. 머리말
지난 글,"사카에 대한고찰"(아래 글 참조)에 이어 스키타이에 대한 연구를 해보고자 한다. 이번 글에서는 구체적인 번역은 생략하고자 한다. 대상 연구 자료는 이글에서는 2024년 위키피디아 자료 Scythians(필자의 네이버 블로그, lainfos, 카테고리, Scythians/Saka 참조)에 한하고자 한다.
따라서 2021년 위키피디아 자료나 History Files 자료에 나타난 보다 넓은 스키타인의 활동영역에 대해서는 스키타이 역사 연구의 마무리부문에서 보다 총체적으로 언급하고자 한다.
사카에 대한 고찰 (tistory.com)
II. 스키타인 (BC 8 c – AD 1c) 이름 및 위치
I) Overview
스키타인은 또한 Scythis, Saka, Sakae, Iskuzai,Askuzai 등으로 불리는 Scythia지역에 사는 고대 유라시아의 유목민이다. 고전적인 의미의 스키타인은 기원전 7세기부터 기원전 3세기까지 흑해위 초원을 지배했다. 그들은 또한 Ponntic Scythians, European Scythians, Western Scyhians으로 불리웠다. 그들은 유라시아 초원에 걸쳐 뻗어 있는 광의의 스키타이 문화의 일부이다. 스키타이 문화의 동부 구성원은 특별히 Sakas라 한다. (아래 자료 참조)
The Scythians (/ˈsɪθiənz, ˈsɪð-/; from Greek Σκύθης, Σκύθοι), also known as Scyths,[1] Saka, Sakae, Iskuzai, or Askuzai, were an ancient nomadic people of Eurasia, inhabiting the region Scythia. Classical Scythians dominated the Pontic steppe from approximately the 7th century BC until the 3rd century BC.[2] They can also be referred to as Pontic Scythians, European Scythians or Western Scythians.[3][4] They were part of the wider Scythian cultures, stretching across the Eurasian Steppe.[5][6] In a broader sense, Scythians has also been used to designate all early Eurasian nomads,[6] although the validity of such terminology is controversial.[5] According to Di Cosmo, other terms such as "Early nomadic" would be preferable.[7] Eastern members of the Scythian cultures are often specifically designated as Sakas.[8]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
기원전 8세기부터, 그들은 서쪽의 카르파티언 산맥에서부터 동쪽의 오르도스 고원까지 전 유라시아 초원을 지배하여, 최초의 중앙아시아 유목민제국을 만들었다. 현재의 우크라이나, 남부 러시아에서, 그들은 스스로를 Scoloti라 불렀으며, 스키타이 귀족으로 알려진 유목민전사에 의해 이끌어졌다. (아래 자료 참조)
The Scythians are generally believed to have been of Iranian (or Iranic; an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group) origin;[9] they spoke a language of the Scythian branch of the Iranian languages,[10] and practiced a variant of ancient Iranian religion.[11] Among the earliest peoples to master mounted warfare,[12] the Scythians replaced the Cimmerians as the dominant power on the Pontic steppe in the 8th century BC.[13] During this time they and related peoples came to dominate the entire Eurasian Steppe from the Carpathian Mountains in the west to Ordos Plateau in the east,[14][15] creating what has been called the first Central Asian nomadic empire.[13][16] Based in what is modern-day Ukraine and southern Russia, they called themselves Scoloti and were led by a nomadic warrior aristocracy known as the Royal Scythians.
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
기원전 7세기에는, 스키타인은 키메리언과 함께 코카서스를 넘어 중동(Middle East)을 자주 유린했으며, 지역의 정치적 발전에 중요한 역할을 했다. BC 650-630 시기에는 서부 이란고원의 Medes왕국을 잠시 지배했으며, 그들의 힘은 이집트국경까지 뻗었다.
In the 7th century BC, the Scythians crossed the Caucasus and frequently raided the Middle East along with the Cimmerians, playing an important role in the political developments of the region.[13][16] Around 650–630 BC, Scythians briefly dominated the Medes of the western Iranian Plateau,[17][18] stretching their power to the borders of Egypt.[12]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
Media에 대한 통제를 잃은 후에, 스키타인은 중동지방의 일에 계속 관여하였는데, 기원전 612년 Nineveh포위에서 앗시리아제국을 파괴하는데 주도적인 역할을 했다. 스키타인은 계속하여 아케메네스제국과 자주 충돌을 하였으며, 기원전 4세기에는 마케도니아에게 튼 패배를 경험하였다. 그후로 그들의 동쪽에 사는 아리안사람들과 관련있는 Sarmatians에 의해 점차 정복되었다.
기원전 2세기 후기에는 크리미아에 있는 그들의 수도 Neapolis가 Mithridates VI에 의해 함락되었으며, 그들의 영토는 Bosporan 왕국에 포함되었다. 이 시기까지 그들은 대부분 헬레니즘화되었다.기원후 3세기까지 Sarmatians과 남은 스키타인은 Alans족에 의해 지배되었으며, 고트족에 의해 제압되었다. 중세 초기까지, 스키타인과 사르마티언은 초기 슬라브족에 의해 대부분 흡수통합되었다. 스키타인은 Ossetians의 민족집단 형성에 있어서 중요했으며, Ossetians은 Alans족의 후예로 믿어진다.
After losing control over Media, they continued intervening in Middle Eastern affairs, playing a leading role in the destruction of the Assyrian Empire in the Sack of Nineveh in 612 BC. The Scythians subsequently engaged in frequent conflicts with the Achaemenid Empire, and suffered a major defeat against Macedonia in the 4th century BC[12] and were subsequently gradually conquered by the Sarmatians, a related Iranian people living to their east.[19]
In the late 2nd century BC, their capital at Scythian Neapolis in the Crimea was captured by Mithridates VI and their territories incorporated into the Bosporan Kingdom.[11] By this time they had been largely Hellenized.
By the 3rd century AD, the Sarmatians and last remnants of the Scythians were dominated by the Alans, and were being overwhelmed by the Goths. By the early Middle Ages, the Scythians and the Sarmatians had been largely assimilated and absorbed by early Slavs.[20][21] The Scythians were instrumental in the ethnogenesis of the Ossetians, who are believed to be descended from the Alans.
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
스키타인은 그리스, 페르시아, 인도, 지나를 연결하는 방대한 무역네트워크인 Silk Road에서 중요한 역할을 했다. 아마도 이들의 문명 번창에 기여했을 것이다. 정착한 금속장인들은 스키타이 금속공예 역사를 형성하는 스키타인의 소지할 수 있는 장식품들을 제조했다. 이러한 물품들은 살아 남아서, 특이한 스키타이예술을 형성했다.
The Scythians played an important part in the Silk Road, a vast trade network connecting Greece, Persia, India and China, perhaps contributing to the prosperity of those civilisations.[23] Settled metalworkers made portable decorative objects for the Scythians, forming a history of Scythian metalworking. These objects survive mainly in metal, forming a distinctive Scythian art.[24]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
과거 저자들은 스키타인 단어를 많은 다른 그룹에 계속 사용했는데, 예를 들어 훈족, 고트족, 튀르크인들, 아바르인, 카자르인 등등이다.
The name of the Scythians survived in the region of Scythia. Early authors continued to use the term "Scythian", applying it to many groups unrelated to the original Scythians, such as Huns, Goths, Turkic peoples, Avars, Khazars, and other unnamed nomads.[11][25] The scientific study of the Scythians is called Scythology.
[출처] <펌>Scythians|작성자 CG Park

Scytho-Siberian World (source : Wikipedia)
II) Names
1. Etymology(어원)
Scythians or Scyths 영어이름의 어원은 고대 그리스 이름 Skuthes, Skutho에서 유래되었는데, 이 그리스말은 스키타이 말로 활쏘는 사람을 뜻하는 Skudata에서 비롯되었다. 헤로도투스에 의하면 그리스어 Skolotoi는 스키타인 왕족들이 스스로를 칭하는 말이었다 한다.
The English name Scythians or Scyths is derived from the Ancient Greek name Skuthēs (Σκυθης) and Skuthoi (Σκυθοι), derived from the Scythian endonym Skuδatā, meaning "archers."[1][17][2][18] Due to a sound change from /δ/ to /l/ in the Scythian language, evolved into the form *Skulatā.[1][2] This designation was recorded in Greek as Skōlotoi (Σκωλοτοι), which, according to Herodotus of Halicarnassus, was the self-designation of the tribe of the Royal Scythians.[18]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
앗시리언은 스키타인의 이름을 Iskuzaya or Askuzaya라 불렀다.
The Assyrians rendered the name of the Scythians as Iškuzaya (𒅖𒆪𒍝𒀀𒀀), māt Iškuzaya (𒆳𒅖𒆪𒍝𒀀𒀀), and awīlū Iškuzaya (𒇽𒅖𒆪𒍝𒀀𒀀),[19][20] or ālu Asguzaya (𒌷𒊍𒄖𒍝𒀀𒀀), māt Askuzaya (𒆳𒊍𒆪𒍝𒀀𒀀), and māt Ašguzaya (𒆳𒀾𒄖𒍝𒀀𒀀).[19][21]
The ancient Persians meanwhile called the Scythians "Sakā who live beyond the (Black) Sea" (𐎿𐎣𐎠 𐏐 𐎫𐎹𐎡𐎹 𐏐 𐎱𐎼𐎭𐎼𐎹, romanized: Sakā tayaiy paradraya) in Old Persian and simply Sakā (Ancient Egyptian: 𓋴𓎝𓎡𓈉, romanized: sk; 𓐠𓎼𓈉, romanized: sꜣg) in Ancient Egyptian, from which was derived the Graeco-Roman name Sacae (Ancient Greek: Σακαι; Latin: Sacae).[22][23]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
2. Modern terminology
스키타인은 보다 넓은 스키토-시베리언집단의 일부인데, 스키토-시베리언 집단은 카자흐스탄, 시베리아, 우랄, 볼가, 그리고 남부지방의 러시아 초원, 그리고 동부 우크라이나의 유라시아 초원을 가로질러 퍼져있었다.
The Scythians were part of the wider Scytho-Siberian world, stretching across the Eurasian Steppes[18][24] of Kazakhstan, the Russian steppes of the Siberian, Ural, Volga and Southern regions, and eastern Ukraine.[25] In a broader sense, Scythians has also been used to designate all early Eurasian nomads,[24] although the validity of such terminology is controversial,[18] and other terms such as "Early nomadic" have been deemed preferable.[26]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
스키타인, 사카, 키메리언은 서로 밀접하게 관련 유목민이지만, 고대 바빌로니언, 고대 페르시안, 고대 그리스인들은 모든 초원 유목민들에 대해, 각각, 키메리언, 사카, 스키타인이란 이름을 사용했다. Edward Gibbon은 스키타인을 유라시아 초원에 있는 다양한 유목민, 반유목민들을 지칭했다.
Although the Scythians, Saka and Cimmerians were closely related nomadic Iranic peoples, and the ancient Babylonians, ancient Persians and ancient Greeks respectively used the names "Cimmerian," "Saka," and "Scythian" for all the steppe nomads, and early modern historians such as Edward Gibbon used the term Scythian to refer to a variety of nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples across the Eurasian Steppe,[27]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
 SAKAS, SCYTHIANS, Pazyryk culture, Khotan, Uyuk culture, Tagar culture, Massagetae, Kangju, Subeshi culture, Ordos culture, Sargat culture, Tasmola culture, Sauromatians, Dahae, Indo-Scythians, Western Satraps, Northern Satraps |
Map of the Scythian ( ) and Saka realms ( ) and their main polities throughout their history.[28][29][30][31] The affiliation of the southeastern-most Subeshi culture and Ordos culture remains uncertain.
- the name "Scythian" in contemporary modern scholarship generally refers to the nomadic Iranic people who from the 7th century BC to the 3rd century BC dominated the steppe and forest-steppe zones to the north of the Black Sea, Crimea, the Kuban valley, as well as the Taman and Kerch peninsulas,[32][23]
- while the name "Saka" is used specifically for their eastern members who inhabited the northern and eastern Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin;[23][33][better source needed][34][35]
- and while the Cimmerians were often described by contemporaries as culturally Scythian, they formed a different tribe from the Scythians proper, to whom the Cimmerians were related, and who also displaced and replaced the Cimmerians in the Pontic Steppe.[36]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
스키타인은 그들의 동쪽에 사는 부족들(사카)과 몇가지 문화적 유사성을 공유했는데, 예를 들면, 특별한 유사한 무기들, 마구, 그리고 스키타이예술의 스키타이 3대 요소이다. 이러한 특징을 나누는 문화를 스키타이 문화라 자주 언급하며, 이 부족들을 스키타인이라 한다. 스키타이 문화와 관련된 부족들은 스키타인 자신들뿐만 아니라, 키메리언, 마사게태, 사카, 사르마티언과 동유럽 숲속 초원에 사는 여러 다른 부족들, 예를 들면, 슬라브족, 발트족, 핀족-위그르족 등도 포함된다.
The Scythians share several cultural similarities with other populations living to their east, in particular similar weapons, horse gear and Scythian art, which has been referred to as the Scythian triad.[18][26] Cultures sharing these characteristics have often been referred to as Scythian cultures, and its peoples called Scythians.[24][37] Peoples associated with Scythian cultures include not only the Scythians themselves, who were a distinct ethnic group,[38] but also Cimmerians, Massagetae, Saka, Sarmatians and various obscure peoples of the East European Forest Steppe,[18][24] such as early Slavs, Balts and Finno-Ugric peoples.[39][40]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
스키타인 단어의 이러한 광범한 정의안에서, 제일 서쪽의 스키타인은 자주 Classical Scythians, Western Scythians, European Scythians 또는 Pontic Scythians이란 표현을 통해 다른 그룹들과 구분된다. 그럼에도 불구하고, 고고학자 Maurits Nanning van Loon은 1966년 키메리언을 지칭하기 위해 Western Scythians이란 표현을 사용했으며, 동방의 스키타인을 원조 스키타인으로 언급했다.
Within this broad definition of the term Scythian, the westernmost Scythians have often been distinguished from other groups through the terms Classical Scythians, Western Scythians, European Scythians or Pontic Scythians.[24] Nevertheless, the archaeologist Maurits Nanning van Loon in 1966 instead used the term Western Scythians to designate the Cimmerians and referred to the Scythians proper as the Eastern Scythians.[41]
Scythologist Askold Ivantchik notes with dismay that the term "Scythian" has been used within both a broad and a narrow context, leading to a good deal of confusion. He reserves the term "Scythian" for the Iranic people dominating the Pontic Steppe from the 7th century BC to the 3rd century BC.[18] Nicola Di Cosmo writes that the broad concept of "Scythian" to describe the early nomadic populations of the Eurasian Steppe is "too broad to be viable," and that the term "early nomadic" is preferable.[26]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
III) Location
1. Early phase in the western steppes
초기 스키타인 그룹과 스키타이 문화는 기원전 1000년대 초기 동유라시아의 초기 사카에서 유래한 것으로 생각된다. 중앙아시아에서 서부 초원으로 이동한 후, 스키타이인은 Araxes강(Herodotus는 Volga강을 그리스인이 부른 이름이라 함, 그러나 현대에서는 Aras river라 함), 코카서스 산맥 그리고 Maeotis호수(=Sea of Azov) 사이에 처음 정착한 후 그들의 왕국을 세웠다.
여기서는 문맥상 Araxes강은 볼가강을 가리키는 것으로 판단된다. (아래 지도 참조)
The earliest Scythian groups and Scythian culture are thought to have emerged with the Early Sakas from eastern Eurasia in the early 1st millennium BC.[42] After migrating out of Central Asia and into the western steppes, the Scythians first settled and established their kingdom in the area between the Araxes, the Caucasus Mountains and the Lake Maeotis.[43][44][45][46][47]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)

Volga river map (source : Wikipedia)
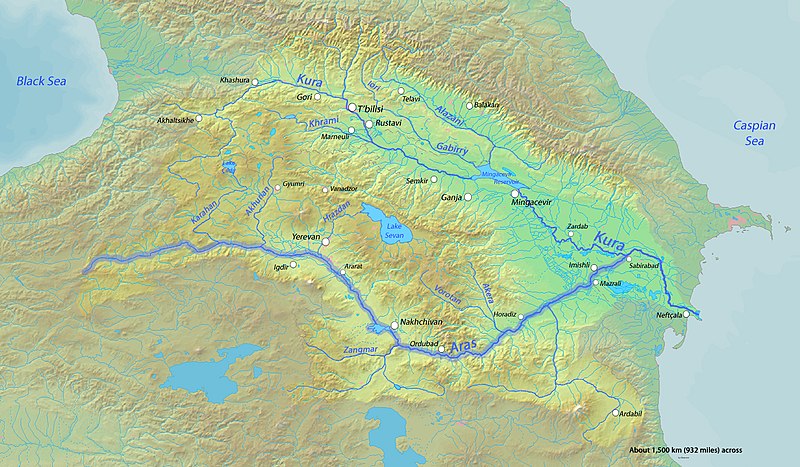
Aras river map (source : Wikipedia)

Sea of Azov (Maeotis lake) and Black Sea map (source : Wikipedia)
(By Created by User:NormanEinstein - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=239407 )

스키타이 왕국의 최대영토 (680 - 600 BC) (자료 : 위키피디아)
2. In West Asia
스키타이 왕들의 본부는 Ciscaucasian 초원에 위치하였다. Ciscaucasia는 the Greater Caucasus를 의미하며, 이 남쪽에는 Transcaucasia가 있다.
In West Asia, the Scythians initially settled in the area between the Araxes and Kura rivers before further expanding into the region to the south of the Kuros river in what is present-day Azerbaijan, where they settled around what is today Mingəçevir, Gəncə and the Muğan plain, and Transcaucasia remained their centre of operations in West Asia until the early 6th century BC,[48][49][50] although this presence in West Asia remained an extension of the Scythian kingdom of the steppes,[18] and the Scythian kings' headquarters were instead located in the Ciscaucasian steppes.[45][46]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
서아시아에서 Media, Mannai, Urartu를 정복하고 키메리언을 패배시킨 후 , 스키타이의 절정기때는, 스키타이 왕국은 서쪽의 아나톨리아, Halys 강으로부터 동쪽으로는 카스피해와 Media의 서쪽 국경까지, 북으로는 Transcaucasia로부터 남으로는 신앗시리아 제국의 북쪽국경까지 뻗는 넓은 영토를 가졌다. (상기 지도 참조)
During the peak of the Scythians' power in West Asia after they had conquered Media, Mannai and Urartu and defeated the Cimmerians, the Scythian kingdom's possessions in the region consisted of a large area extending from the Halys river in Anatolia in the west to the Caspian Sea and the western borders of Media in the east, and from Transcaucasia in the north to the northern borders of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in the south.[51][52][53]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
3. In the Pontic steppe
Pontic steppe의 스키타이왕국의 영토는 동쪽의 Don강으로부터 서쪽의 다뉴브강, 흑해 연안의 바로 위 유목민들이 살았던 나무 없는 초원의 땅을 포함하고, 이 나무없는 초원 북쪽의 농민들이 사는 기름진 흑토의 숲초원도 포함한다. 스키타이 왕국의 북쪽 국경은 삼림지대이다.
The territory of the Scythian kingdom of the Pontic steppe extended from the Don river in the east to the Danube river in the west, and covered the territory of the treeless steppe immediately north of the Black Sea's coastline, which was inhabited by nomadic pastoralists, as well as the fertile black-earth forest-steppe area to the north of the treeless steppe, which was inhabited by an agricultural population,[55][47][56][57] and the northern border of this Scythian kingdom were the dedicuous woodlands.[58]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
몇개의 강이 이 지역을 가로질러 남쪽으로 흘러 흑해로 들어 간다. 그중 가장 긴 강이 드네프로강(Borysthenes)이며, 강의 물고기, 최선의 목축업, 강가에 위치한 매우 기름진 땅, 등으로 스키타에서 가장 풍요로운 강이며, 그럼에도 불구하고 물은 가장 깨끗하다. 그래서 그리스-로마 학자들은 이집트의 나일강에 비유했다. 스키타이의 다른 중요한 강들은 아래와 같다 : Istros (Danube), Tyras (Dnister), Hypanis (Southern Buh), Panticapes (Inhulets), Hypacyris, Gerrhus, and Tanais (Don).
Several rivers flowed southwards across this region and emptied themselves into the Black Sea, of which the largest one was the Borysthenes (Dnipro), which was the richest river in Scythia, with most of the fish living in it, and the best pastures and most fertile lands being located on its banks, while its water was the cleanest; due to this, Graeco-Roman authors compared it to the Nile in Egypt. Other important rivers of Scythia were the:[58][59]
- Istros (Danube),
- Tyras (Dnister),
- Hypanis (Southern Buh),
- Panticapes (Inhulets),
- Hypacyris,
- Gerrhus,
- and Tanais (Don).
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
스키타이 흑해위 초원지대 지역은 숲으로 덮혀 있어 그리스인들은 Hylaea(=woodland) country라 이름지어졌다. 이 지역은 현대의 Kherson영토를 따라 있는 드네프로강 하류지역이다.
The region within the Scythian Pontic realm which was covered with forests was named by the Greeks as the country of Hylaea (Ancient Greek: Υλαια, romanized: Hulaia, lit. 'the Woodland'), and consisted of the region of the lower Dnipro river along the territory of what is modern-day Kherson.[60][61]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
고대 서아시아와 그리스 자료는 스키타이 범위에 Ciscaucasia(Greater caucasia)를 포함했다. 그러나 Ciscaucasia는 기원전 5세기에는 더 이상 스키타이지역이 아니고 돈강이 가장 동쪽끝이 되었다.
Earlier ancient West Asian and Greek sources also included Ciscaucasia within the confines of Scythia. However, Ciscaucasia was no longer part of Scythia by the 5th century BC, and the Don river formed its easternmost limit.[62]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
4. Little Scythia
기원전 3세기이후는, 스키타이 영역은 두 조그만 나라에 제한되었는데, 각각 Little Scythia라 불렸으며, 각각 Dobruja와 크리미아에 위치했다.
After the 3rd century BC, Scythian territory became restricted to two small states, each called "Little Scythia," respectively located in Dobruja and Crimea:
- in Dobruja, the Scythian kingdom's territory stretched from Tyras, or even Pontic Olbia in the north, to Odessus in the south;[63]
- in Crimea, the Scythian kingdom covered a limited territory which included the steppes and foothills of Crimea from contemporary Taurida, the lower Dnieper River, and the lower Southern Bug rivers.[47]
(source : Scythians, Wikipedia, 2024)
'한국의 역사 > 고조선' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 스키타인 역사(3) : Late Scythian (BC 200 - AD 3C 중반) (0) | 2024.06.14 |
|---|---|
| 스키타인의 역사(2) - Classical Scythian (BC 500 - 300 BC) (0) | 2024.06.08 |
| 스키타인 역사(1) - Early Scythian (BC 12 c - BC 500) (0) | 2024.05.10 |
| 신석기 시대 동북아시아의 홍산문화와 관련된 앙소문화 고찰 (0) | 2024.03.25 |
| 12환국 시대 이전 구석기 시대 유라시아 인류 이동 역사 (0) | 2024.03.20 |