I. 사카인의 정체
The Saka (Old Persian:𐎿𐎣𐎠 Sakā; Kharoṣṭhī: 𐨯𐨐 Saka; Ancient Egyptian: 𓋴𓎝𓎡𓈉 sk, 𓐠𓎼𓈉 sꜣg; Chinese: 塞, old *Sək, mod. Sè, Sāi), Shaka (Sanskrit (Brāhmī): 𑀰𑀓., Śaka; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): शक Śaka, शाक Śāka), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: Σάκαι Sákai; Latin: Sacae) were a group of nomadic Eastern Iranian peoples who historically inhabited the northern and eastern Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin.[7][8]
The Sakas were closely related to the Scythians, and both groups formed part of the wider Scythian cultures,[9] through which they ultimately derived from the earlier Andronovo, Sintashta and Srubnaya cultures, with secondary influence from the BMAC, and since the Iron Age, also East Asian genetic influx,[10][11] with the Saka language forming part of the Scythian phylum, one of the Eastern Iranian languages. However, the Sakas of the Asian steppes are to be distinguished from the Scythians of the Pontic Steppe;[8][12] and although the ancient Persians, ancient Greeks, and ancient Babylonians respectively used the names "Saka," "Scythian," and "Cimmerian" for all the steppe nomads, the name "Saka" is used specifically for the ancient nomads of the eastern steppe, while "Scythian" is used for the related group of nomads living in the western steppe.[8][13][14] While the Cimmerians were often described by contemporaries as culturally Scythian, they may have differed ethnically from the Scythians proper, to whom the Cimmerians were related, and who also displaced and replaced the Cimmerians.[15]
Prominent archaeological remains of the Sakas include Arzhan,[16] Tunnug,[17] the Pazyryk burials,[18] the Issyk kurgan, Saka Kurgan tombs,[19] the Barrows of Tasmola[20] and possibly Tillya Tepe.
[출처] <펌>Saka - wikipedia(Feb 2024)|작성자 CG Park
Derived from an Iranian verbal root sak-, "go, roam" (related to "seek") and thus meaning "nomad" was the term Sakā, from which came the names:
- Old Persian: 𐎿𐎣𐎠 Sakā, used by the ancient Persians to designate all nomads of the Eurasian steppe, including the Pontic Scythians[26]
- Ancient Greek: Σάκαι Sákai
- Latin: Sacae
- Sanskrit: शक Śaka
- Old Chinese: 塞 Sək[27][28][29]
From the Indo-European root (s)kewd-, meaning "propel, shoot" (and from which was also derived the English word shoot), of which *skud- is the zero-grade form, was descended the Scythians' self-name reconstructed by Szemerényi as *Skuδa (roughly "archer")
[출처] <펌>Saka - wikipedia(Feb 2024)|작성자 CG Park
Although the Scythians, Saka and Cimmerians were closely related nomadic Iranic peoples, and the ancient Babylonians, ancient Persians and ancient Greeks respectively used the names "Cimmerian," "Saka," and "Scythian" for all the steppe nomads, and early modern historians such as Edward Gibbon used the term Scythian to refer to a variety of nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples across the Eurasian Steppe,
- the name "Scythian" in contemporary modern scholarship generally refers to the nomadic Iranic people who from the 7th century BC to the 3rd century BC dominated the steppe and forest-steppe zones to the north of the Black Sea, Crimea, the Kuban valley, as well as the Taman and Kerch peninsulas,[33][34]
- while the name "Saka" is used specifically for their eastern members who inhabited the northern and eastern Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin;[34][35]
- [출처] <펌>Saka - wikipedia(Feb 2024)|작성자 CG Park
Identification[edit]
The name Sakā was used by the ancient Persian to refer to all the Iranian nomadic tribes living to the north of their empire, including both those who lived between the Caspian Sea and the Hungry steppe, and those who lived to the north of the Danube and the Black Sea. The Assyrians meanwhile called these nomads the Ishkuzai (Akkadian: Iškuzaya[36][37]) or Askuzai (Akkadian: Asguzaya, mat Askuzaya, mat Ášguzaya[36][38]), and the Ancient Greeks called them Skuthai (Ancient Greek: Σκύθης Skúthēs, Σκύθοι Skúthoi, Σκύθαι Skúthai).[39]
For the Achaemenids, there were three types of Sakas: the Sakā tayai paradraya ("beyond the sea", presumably between the Greeks and the Thracians on the Western side of the Black Sea), the Sakā Tigraxaudā (the Massagetae, "with pointed caps"), the Sakā haumavargā ("Hauma drinkers", furthest East). Soldiers of the Achaemenid army, Xerxes I tomb detail, circa 480 BC.[40]
The Achaemenid inscriptions initially listed a single group of Sakā. However, following Darius I's campaign of 520 to 518 BC against the Asian nomads, they were differentiated into two groups, both living in Central Asia to the east of the Caspian Sea:[39][41]
- the Sakā tigraxaudā (𐎿𐎣𐎠 𐏐 𐎫𐎡𐎥𐎼𐎧𐎢𐎭𐎠) – "Sakā who wear pointed caps," who were also known as the Massagetae.[42][43]
- the Sakā haumavargā (𐎿𐎣𐎠 𐏐 𐏃𐎢𐎶𐎺𐎼𐎥𐎠) – interpreted as "Sakā who lay hauma (around the fire)",[44] which can be interpreted as "Saka who revere hauma."[45]
A third name was added after the Darius's campaign north of the Danube:[39]
- the Sakā tayaiy paradraya (𐎿𐎣𐎠 𐏐 𐎫𐎹𐎡𐎹 𐏐 𐎱𐎼𐎭𐎼𐎹) – "the Sakā who live beyond the (Black) Sea," who were the Pontic Scythians of the East European steppes
- [출처] <펌>Saka - wikipedia(Feb 2024)|작성자 CG Park
An additional term is found in two inscriptions elsewhere:[46][39]
- the Sakaibiš tayaiy para Sugdam (𐎿𐎣𐎡𐎲𐎡𐏁 𐏐 𐎫𐎹𐎡𐎹 𐏐 𐎱𐎼 𐏐 𐎿𐎢𐎥𐎭𐎶) – "Saka who are beyond Sogdia", a term was used by Darius for the people who formed the north-eastern limits of his empire at the opposite end to the satrapy of Kush (the Ethiopians).[47][48] These Sakaibiš tayaiy para Sugdam have been suggested to have been the same people as the Sakā haumavargā[49]
Moreover, Darius the Great's Suez Inscriptions mention two groups of Saka:[50][51]
- the Sꜣg pḥ (𓐠𓎼𓄖𓈉) – "Sakā of the Marshes"
- the Sk tꜣ (𓋴𓎝𓎡𓇿𓈉) – "Sakā of the Land"
The scholar David Bivar had tentatively identified the Sk tꜣ with the Sakā haumavargā,[52] and John Manuel Cook had tentatively identified the Sꜣg pḥ with the Sakā tigraxaudā.[49] More recently, the scholar Rüdiger Schmitt has suggested that the Sꜣg pḥ and the Sk tꜣ might have collectively designated the Sakā tigraxaudā/Massagetae.[53]
The Achaemenid king Xerxes I listed the Saka coupled with the Dahā (𐎭𐏃𐎠) people of Central Asia,[47][49][46] who might possibly have been identical with the Sakā tigraxaudā.[54][55][56]
[출처] <펌>Saka - wikipedia(Feb 2024)|작성자 CG Park
Modern terminology[edit]
See also: Scythian cultures
Although the ancient Persians, ancient Greeks, and ancient Babylonians respectively used the names "Saka," "Scythian," and "Cimmerian" for all the steppe nomads, modern scholars now use the term Saka to refer specifically to Iranian peoples who inhabited the northern and eastern Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin;[7][57][8][14] and while the Cimmerians were often described by contemporaries as culturally Scythian, they may have differed ethnically from the Scythians proper, to whom the Cimmerians were related, and who also displaced and replaced the Cimmerians.[15]
[출처] <펌>Saka - wikipedia(Feb 2024)|작성자 CG Park
The Scythian/Saka cultures emerged on the Eurasian Steppe at the dawn of the Iron Age in the early 1st millennium BC. Their origins has long been a source of debate among archaeologists.[64] The Pontic–Caspian steppe was initially thought to have been their place of origin, until the Soviet archaeologist Aleksey Terenozhkin suggested a Central Asian origin.[65][66]
Archaeological evidence now tends to suggest that the origins of Scythian culture, characterized by its kurgans (a type of burial mound) and its Animal style of the 1st millennium BC, are to be found among Eastern Scythians rather than their Western counterparts: eastern kurgans are older than western ones (such as the Altai kurgan Arzhan 1 in Tuva), and elements of the Animal style are first attested in areas of the Yenisei river and modern-day China in the 10th century BC.[67] Genetic evidence corroborates archaeological findings, suggesting an initial eastwards expansion of Western Steppe Herders towards the Altai region and Western Mongolia, spreading Iranian languages, and subsequent contact episodes with local Siberian and Eastern Asian populations, giving rise to the initial (Eastern) Scythian material cultures (Saka). It was however also found that the various later Scythian sub-groups of the Eurasian Steppe had local origins; different Scythian groups arose locally through cultural adaption, rather than via migration patterns from East-to-West or West-to-East.[68][69][70][11]
[출처] <펌>Saka - wikipedia(Feb 2024)|작성자 CG Park
II. 사카인의 활동 지역

Map of Saka cultures (800-200 BC)
Map of Mongolia (Early iron age) (1000-200 BC)
Location[edit]
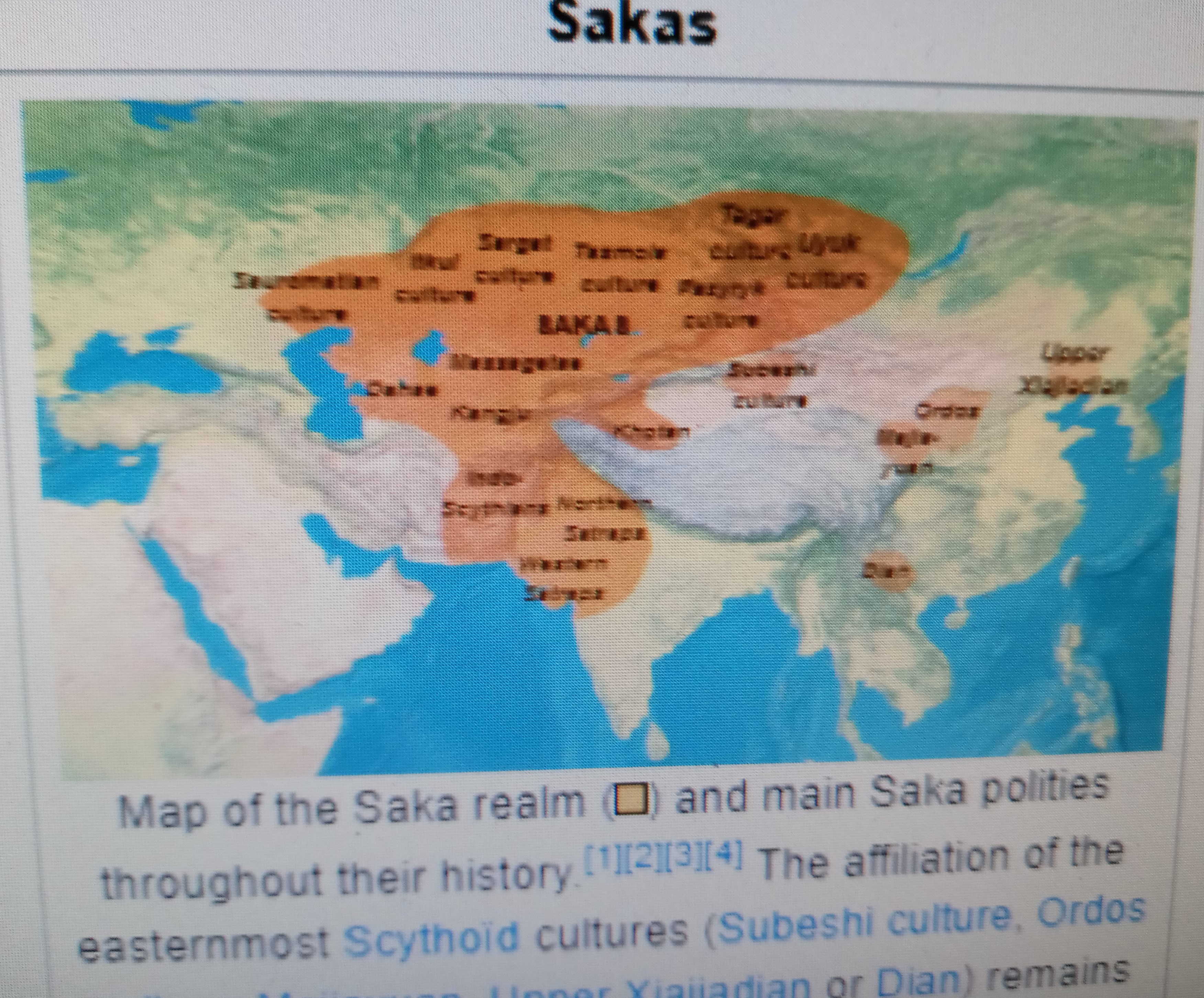
The Sakas ( ), and main Asian polities, circa 325 BC.[58][2][3][59]
The Sakā tigraxaudā and Sakā haumavargā both lived in the steppe and highland areas located in northern Central Asia and to the east of the Caspian Sea.[39][41][60]
The Sakā tigraxaudā/Massagetae more specifically lived around Chorasmia[61] and in the lowlands of Central Asia located to the east of the Caspian Sea and the south-east of the Aral Sea, in the Kyzylkum Desert and the Ustyurt Plateau, most especially between the Araxes and Iaxartes rivers.[54][53] The Sakā tigraxaudā/Massagetae could also be found in the Caspian Steppe.[42] The imprecise description of where the Massagetae lived by ancient authors has however led modern scholars to ascribe to them various locations, such as the Oxus delta, the Iaxartes delta, between the Caspian and Aral seas or forther to the north or north-east, but without basing these suggestions on any conclusive arguments.[53] Other locations assigned to the Massagetae include the area corresponding to modern-day Turkmenistan.[62]
The Sakā haumavargā lived around the Pamir Mountains and the Ferghana Valley.[61]
The Sakaibiš tayaiy para Sugdam, who may have been identical with the Sakā haumavargā, lived on the north-east border of the Achaemenid Empire on the Iaxartes river.[39]
Some other Saka groups lived to the east of the Pamir Mountains and to the north of the Iaxartes river,[60] as well as in the regions corresponding to modern-day Qirghizia, Tian Shan, Altai, Tuva, Mongolia, Xinjiang, and Kazakhstan.[61]
The Sək, that is the Saka who were in contact with the Chinese, inhabited the Ili and Chu valleys of modern Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan, which was called the "land of the Sək", i.e. "land of the Saka", in the Book of Han.[63]
III. 사카인의 역사
History[edit]
Origins[edit]
Arzhan kurgans (9–7th century BC)
Arzhan kurgan and early Saka artifacts, dated to 8–7th century BC
The Scythian/Saka cultures emerged on the Eurasian Steppe at the dawn of the Iron Age in the early 1st millennium BC. Their origins has long been a source of debate among archaeologists.[64] The Pontic–Caspian steppe was initially thought to have been their place of origin, until the Soviet archaeologist Aleksey Terenozhkin suggested a Central Asian origin.[65][66]
Archaeological evidence now tends to suggest that the origins of Scythian culture, characterized by its kurgans (a type of burial mound) and its Animal style of the 1st millennium BC, are to be found among Eastern Scythians rather than their Western counterparts: eastern kurgans are older than western ones (such as the Altai kurgan Arzhan 1 in Tuva), and elements of the Animal style are first attested in areas of the Yenisei river and modern-day China in the 10th century BC.[67] Genetic evidence corroborates archaeological findings, suggesting an initial eastwards expansion of Western Steppe Herders towards the Altai region and Western Mongolia, spreading Iranian languages, and subsequent contact episodes with local Siberian and Eastern Asian populations, giving rise to the initial (Eastern) Scythian material cultures (Saka). It was however also found that the various later Scythian sub-groups of the Eurasian Steppe had local origins; different Scythian groups arose locally through cultural adaption, rather than via migration patterns from East-to-West or West-to-East.[68][69][70][11]
The Sakas spoke a language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. The Pazyryk burials of the Pazyryk culture in the Ukok Plateau in the 4th and 3rd centuries BC are thought to be of Saka chieftains.[71][72][73] These burials show striking similarities with the earlier Tarim mummies at Gumugou.[72] The Issyk kurgan of south-eastern Kazakhstan,[73] and the Ordos culture of the Ordos Plateau has also been connected with the Saka.[74] It has been suggested that the ruling elite of the Xiongnu was of Saka origin, or at least significantly influeced by their Eastern Iranian neighbours.[75][76] Some scholars contend that in the 8th century BC, a Saka raid from the Altai may be "connected" with a raid on Zhou China.[77]
Early history[edit]

Sakā Tigraxaudā tribute bearers to the Achaemenid Empire, Apadana, Staircase 12.[78]
The Saka are attested in historical and archaeological records dating to around the 8th century BC.[79]
The Saka tribe of the Massagetae/Tigraxaudā rose to power in the 8th to 7th centuries BC, when they migrated from the east into Central Asia,[53] from where they expelled the Scythians, another nomadic Iranian tribe to whom they were closely related, after which they came to occupy large areas of the region beginning in the 6th century BC.[42] The Massagetae forcing the Early Scythians to the west across the Araxes river and into the Caucasian and Pontic steppes started a significant movement of the nomadic peoples of the Eurasian Steppe,[80] following which the Scythians displaced the Cimmerians and the Agathyrsi, who were also nomadic Iranian peoples closely related to the Massagetae and the Scythians, conquered their territories,[80][81][42][82][83][84] and invaded Western Asia, where their presence had an important role in the history of the ancient civilisations of Mesopotamia, Anatolia, Egypt, and Iran.[82]
During the 7th century BC itself, Saka presence started appearing in the Tarim Basin region.[79]
According to the ancient Greek historian Diodorus Siculus, the Parthians rebelled against the Medes during the reign of Cyaxares, after which the Parthians put their country and capital city under the protection of the Sakas. This was followed by a long war opposing the Medes to the Saka, the latter of whom were led by the queen Zarinaea. At the end of this war, the Parthians accepted Median rule, and the Saka and the Medes made peace.[85][86][87]
Captured Saka king Skunkha, from Mount Behistun, Iran, Achaemenid stone relief from the reign of Darius I (r. 522–486 BC)
The Sakas as subjects of the Achaemenid Empire on the statue of Darius I, circa 500 BC.
According to the Greek historian Ctesias, once the Persian Achaemenid Empire's founder, Cyrus, had overthrown his grandfather the Median king Astyages, the Bactrians accepted him as the heir of Astyages and submitted to him, after which he founded the city of Cyropolis on the Iaxartes river as well as seven fortresses to protect the northern frontier of his empire against the Saka. Cyrus then attacked the Sakā haumavargā, initially defeated them and captured their king, Amorges. After this, Amorges's queen, Sparethra, defeated Cyrus with a large army of both men and women warriors and captured Parmises, the brother-in-law of Cyrus and the brother of his wife Amytis, as well as Parmises's three sons, whom Sparethra exchanged in return for her husband, after which Cyrus and Amorges became allies, and Amorges helped Cyrus conquer Lydia.[88][89][90][91][92][93]
Cyrus, accompanied by the Sakā haumavargā of his ally Amorges, later carried out a campaign against the Massagetae/Sakā tigraxaudā in 530 BC.[53] According to Herodotus, Cyrus captured a Massagetaean camp by ruse, after which the Massagetae queen Tomyris led the tribe's main force against the Persians, defeated them, and placed the severed head of Cyrus in a sack full of blood. Some versions of the records of the death of Cyrus named the Derbices, rather than the Massagetae, as the tribe against whom Cyrus died in battle, because the Derbices were a member tribe of the Massagetae confederation or identical with the whole of the Massagetae.[94][53] After Cyrus had been mortally wounded by the Derbices/Massagetae, Amorges and his Sakā haumavargā army helped the Persian soldiers defeat them. Cyrus told his sons to respect their own mother as well as Amorges above everyone else before dying.[93]
Possibly shortly before the 520s BC, the Saka expanded into the valleys of the Ili and Chu in eastern Central Asia.[63] Around 30 Saka tombs in the form of kurgans (burial mounds) have also been found in the Tian Shan area dated to between 550 and 250 BC.[79]
Darius I waged wars against the eastern Sakas during a campaign of 520 to 518 BC where, according to his inscription at Behistun, he conquered the Massagetae/Sakā tigraxaudā, captured their king Skunxa, and replaced him with a ruler who was loyal to Achaemenid rule.[53][93][95] The territories of the Saka were absorbed into the Achaemenid Empire as part of Chorasmia that included much of the territory between the Oxus and the Iaxartes rivers,[96] and the Saka then supplied the Achaemenid army with a large number of mounted bowmen.[97] According to Polyaenus, Darius fought against three armies led by three kings, respectively named Sacesphares, Amorges or Homarges, and Thamyris, with Polyaenus's account being based on accurate Persian historical records.[93][98][99] After Darius's administrative reforms of the Achaemenid Empire, the Sakā tigraxaudā were included within the same tax district as the Medes.[100]
During the period of Achaemenid rule, Central Asia was in contact with Saka populations who were themselves in contact with China.[101]
After Alexander the Great conquered the Achaemenid Empire, the Saka resisted his incursions into Central Asia.[57]
At least by the late 2nd century BC, the Sakas had founded states in the Tarim Basin.[24]
--------------------- x x ----------------------
Kingdoms in the Tarim Basin[edit]
Kingdom of Khotan[edit]
Main article: Kingdom of Khotan

Saka hunter with bow, 2nd-1st century BC, Almaty, Kazakhstan
The Kingdom of Khotan was a Saka city state on the southern edge of the Tarim Basin. As a consequence of the Han–Xiongnu War spanning from 133 BC to 89 AD, the Tarim Basin (now Xinjiang, Northwest China), including Khotan and Kashgar, fell under Han Chinese influence, beginning with the reign of Emperor Wu of Han (r. 141–87 BC).[102][103]

Coin of Gurgamoya, king of Khotan. Khotan, first century.
Obv: Kharosthi legend, "Of the great king of kings, king of Khotan, Gurgamoya.
Rev: Chinese legend: "Twenty-four grain copper coin". British Museum
Archaeological evidence and documents from Khotan and other sites in the Tarim Basin provided information on the language spoken by the Saka.[104][105] The official language of Khotan was initially Gandhari Prakrit written in Kharosthi, and coins from Khotan dated to the 1st century bear dual inscriptions in Chinese and Gandhari Prakrit, indicating links of Khotan to both India and China.[106] Surviving documents however suggest that an Iranian language was used by the people of the kingdom for a long time. Third-century AD documents in Prakrit from nearby Shanshan record the title for the king of Khotan as hinajha (i.e. "generalissimo"), a distinctively Iranian-based word equivalent to the Sanskrit title senapati, yet nearly identical to the Khotanese Saka hīnāysa attested in later Khotanese documents.[106] This, along with the fact that the king's recorded regnal periods were given as the Khotanese kṣuṇa, "implies an established connection between the Iranian inhabitants and the royal power," according to the Professor of Iranian Studies Ronald E. Emmerick.[106] He contended that Khotanese-Saka-language royal rescripts of Khotan dated to the 10th century "makes it likely that the ruler of Khotan was a speaker of Iranian."[106] Furthermore, he argued that the early form of the name of Khotan, hvatana, is connected semantically with the name Saka.[106]
The region once again came under Chinese suzerainty with the campaigns of conquest by Emperor Taizong of Tang (r. 626–649).[107] From the late eighth to ninth centuries, the region changed hands between the rival Tang and Tibetan Empires.[108][109] However, by the early 11th century the region fell to the Muslim Turkic peoples of the Kara-Khanid Khanate, which led to both the Turkification of the region as well as its conversion from Buddhism to Islam.

A document from Khotan written in Khotanese Saka, part of the Eastern Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages, listing the animals of the Chinese zodiac in the cycle of predictions for people born in that year; ink on paper, early 9th century
Later Khotanese-Saka-language documents, ranging from medical texts to Buddhist literature, have been found in Khotan and Tumshuq (northeast of Kashgar).[104] Similar documents in the Khotanese-Saka language dating mostly to the 10th century have been found in the Dunhuang manuscripts.[110]
Although the ancient Chinese had called Khotan Yutian (于闐), another more native Iranian name occasionally used was Jusadanna (瞿薩旦那), derived from Indo-Iranian Gostan and Gostana, the names of the town and region around it, respectively.[111]
Shule Kingdom[edit]
Main article: Shule Kingdom
Much like the neighboring people of the Kingdom of Khotan, the people of Kashgar, the capital of Shule, spoke Saka, one of the Eastern Iranian languages.[112] According to the Book of Han, the Saka split and formed several states in the region. These Saka states may include two states to the northwest of Kashgar, Tumshuq to its northeast, and Tushkurgan south in the Pamirs.[113] Kashgar also conquered other states such as Yarkand and Kucha during the Han dynasty, but in its later history, Kashgar was controlled by various empires, including Tang China,[114][115][116] before it became part of the Turkic Kara-Khanid Khanate in the 10th century. In the 11th century, according to Mahmud al-Kashgari, some non-Turkic languages like Kanchaki and Sogdian were still used in some areas in the vicinity of Kashgar,[117] and Kanchaki is thought to belong to the Saka language group.[113] It is believed that the Tarim Basin was linguistically Turkified before the 11th century ended.[118]
Southern migrations[edit]

Model of a Saka/Kangju cataphract armour with neck-guard, from Khalchayan. 1st century BC. Museum of Arts of Uzbekistan, nb 40.[119]
The Saka were pushed out of the Ili and Chu River valleys by the Yuezhi.[120][21][22] An account of the movement of these people is given in Sima Qian's Records of the Grand Historian. The Yuehzhi, who originally lived between Tängri Tagh (Tian Shan) and Dunhuang of Gansu, China,[121] were assaulted and forced to flee from the Hexi Corridor of Gansu by the forces of the Xiongnu ruler Modu Chanyu, who conquered the area in 177–176 BC.[122][123][124][125][126][127] In turn the Yuehzhi were responsible for attacking and pushing the Sai (i.e. Saka) west into Sogdiana, where, between 140 and 130 BC, the latter crossed the Syr Darya into Bactria. The Saka also moved southwards toward the Pamirs and northern India, where they settled in Kashmir, and eastward, to settle in some of the oasis-states of Tarim Basin sites, like Yanqi (焉耆, Karasahr) and Qiuci (龜茲, Kucha).[128][129] The Yuehzhi, themselves under attacks from another nomadic tribe, the Wusun, in 133–132 BC, moved, again, from the Ili and Chu valleys, and occupied the country of Daxia, (大夏, "Bactria").[63][130]

The Heavenly Horse, commonly known as the Ferghana Horse, is an ancient ceremonial bronze finial. It originates from Bactria, dating back to the 4th-1st century BC, and was skillfully crafted by Saka tribes.
------------------------ x x ------------------------------
The ancient Greco-Roman geographer Strabo noted that the four tribes that took down the Bactrians in the Greek and Roman account – the Asioi, Pasianoi, Tokharoi and Sakaraulai – came from land north of the Syr Darya where the Ili and Chu valleys are located.[131][63] Identification of these four tribes varies, but Sakaraulai may indicate an ancient Saka tribe, the Tokharoi is possibly the Yuezhi, and while the Asioi had been proposed to be groups such as the Wusun or Alans.[131][132]
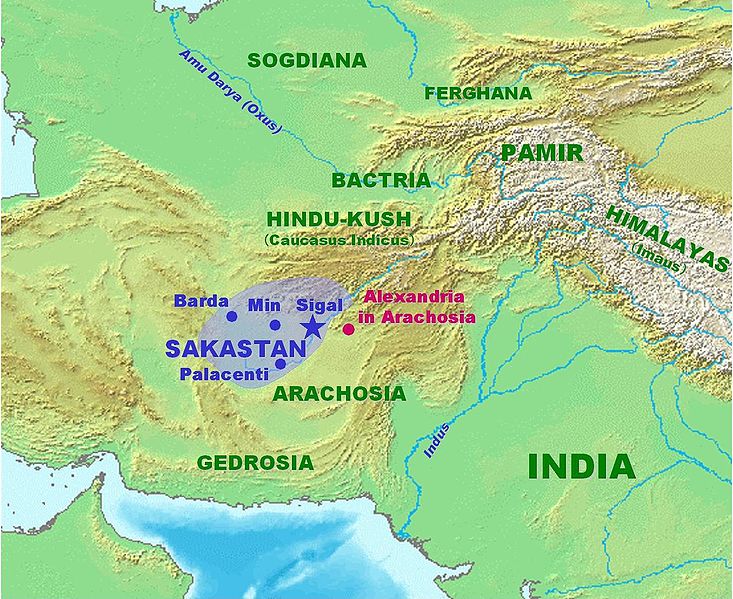
Map of Sakastan ("Land of the Sakas"), where the Sakas resettled c. 100 BC
René Grousset wrote of the migration of the Saka: "the Saka, under pressure from the Yueh-chih [Yuezhi], overran Sogdiana and then Bactria, there taking the place of the Greeks." Then, "Thrust back in the south by the Yueh-chih," the Saka occupied "the Saka country, Sakastana, whence the modern Persian Seistan."[131] Some of the Saka fleeing the Yuezhi attacked the Parthian Empire, where they defeated and killed the kings Phraates II and Artabanus.[120] These Sakas were eventually settled by Mithridates II in what become known as Sakastan.[120] According to Harold Walter Bailey, the territory of Drangiana (now in Afghanistan and Pakistan) became known as "Land of the Sakas", and was called Sakastāna in the Persian language of contemporary Iran, in Armenian as Sakastan, with similar equivalents in Pahlavi, Greek, Sogdian, Syriac, Arabic, and the Middle Persian tongue used in Turfan, Xinjiang, China.[104] This is attested in a contemporary Kharosthi inscription found on the Mathura lion capital belonging to the Saka kingdom of the Indo-Scythians (200 BC – 400 AD) in North India,[104] roughly the same time the Chinese record that the Saka had invaded and settled the country of Jibin 罽賓 (i.e. Kashmir, of modern-day India and Pakistan).[133]
Iaroslav Lebedynsky and Victor H. Mair speculate that some Sakas may also have migrated to the area of Yunnan in southern China following their expulsion by the Yuezhi. Excavations of the prehistoric art of the Dian Kingdom of Yunnan have revealed hunting scenes of Caucasoid horsemen in Central Asian clothing.[134] The scenes depicted on these drums sometimes represent these horsemen practising hunting. Animal scenes of felines attacking oxen are also at times reminiscent of Scythian art both in theme and in composition.[135] Migrations of the 2nd and 1st century BC have left traces in Sogdia and Bactria, but they cannot firmly be attributed to the Saka, similarly with the sites of Sirkap and Taxila in ancient India. The rich graves at Tillya Tepe in Afghanistan are seen as part of a population affected by the Saka.[136]
The Shakya clan of India, to which Gautama Buddha, called Śākyamuni "Sage of the Shakyas", belonged, were also likely Sakas, as Michael Witzel[137] and Christopher I. Beckwith[138] have alleged. The scholar Bryan Levman however criticised this hypothesis for resting on slim to no evidence, and maintains that the Shakyas were a population native to the north-east Gangetic plain who were unrelated to Iranic Sakas.[139]
Indo-Scythians[edit]
Main article: Indo-Scythians

Head of a Saka warrior, as a defeated enemy of the Yuezhi, from Khalchayan, northern Bactria, 1st century BC.[140][141][142]
The region in modern Afghanistan and Iran where the Saka moved to became known as "land of the Saka" or Sakastan.[104] This is attested in a contemporary Kharosthi inscription found on the Mathura lion capital belonging to the Saka kingdom of the Indo-Scythians (200 BC – 400 AD) in northern India,[104] roughly the same time the Chinese record that the Saka had invaded and settled the country of Jibin 罽賓 (i.e. Kashmir, of modern-day India and Pakistan).[133] In the Persian language of contemporary Iran the territory of Drangiana was called Sakastāna, in Armenian as Sakastan, with similar equivalents in Pahlavi, Greek, Sogdian, Syriac, Arabic, and the Middle Persian tongue used in Turfan, Xinjiang, China.[104] The Sakas also captured Gandhara and Taxila, and migrated to North India.[143] The most famous Indo-Scythian king was Maues.[144] An Indo-Scythian kingdom was established in Mathura (200 BC – 400 AD).[104][23] Weer Rajendra Rishi, an Indian linguist, identified linguistic affinities between Indian and Central Asian languages, which further lends credence to the possibility of historical Sakan influence in North India.[143][145] According to historian Michael Mitchiner, the Abhira tribe were a Saka people cited in the Gunda inscription of the Western Satrap Rudrasimha I dated to AD 181.[146]
Later Saka polities

- The Indo-Scythians ruled in northwestern South Asia from circa 100 BC
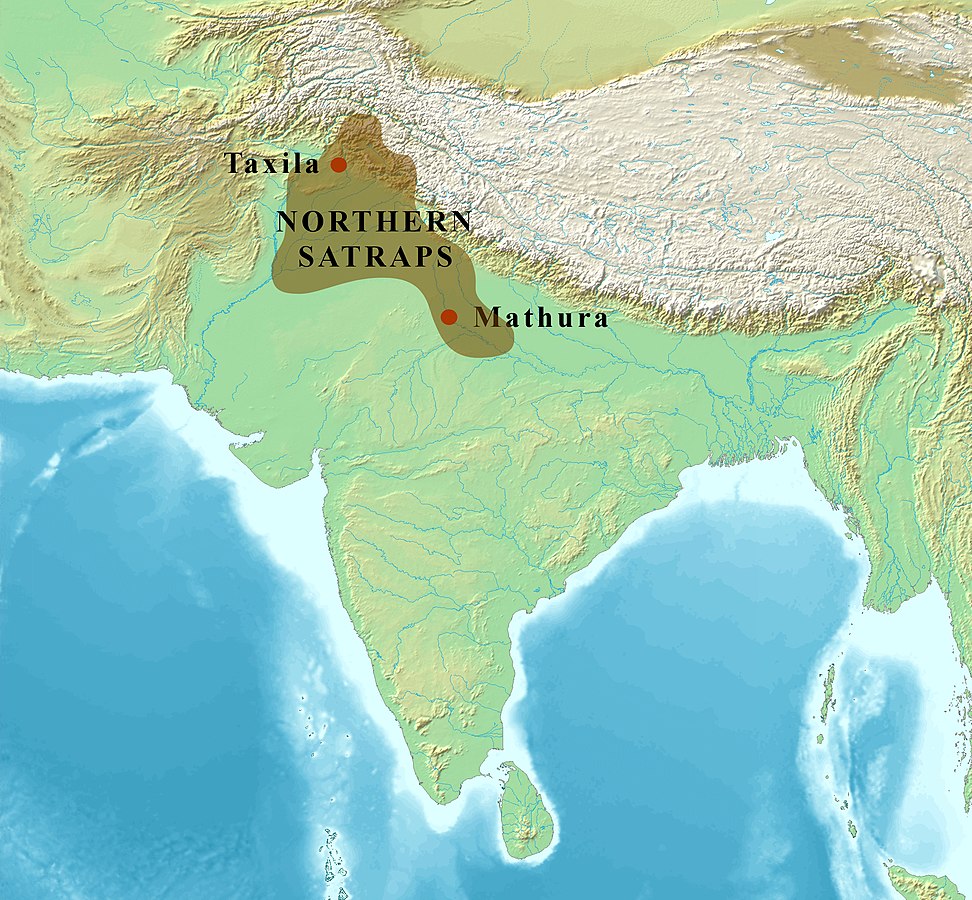
- The Northern Satraps ruled in northern India until their replacement by the Kushans circa 150 AD
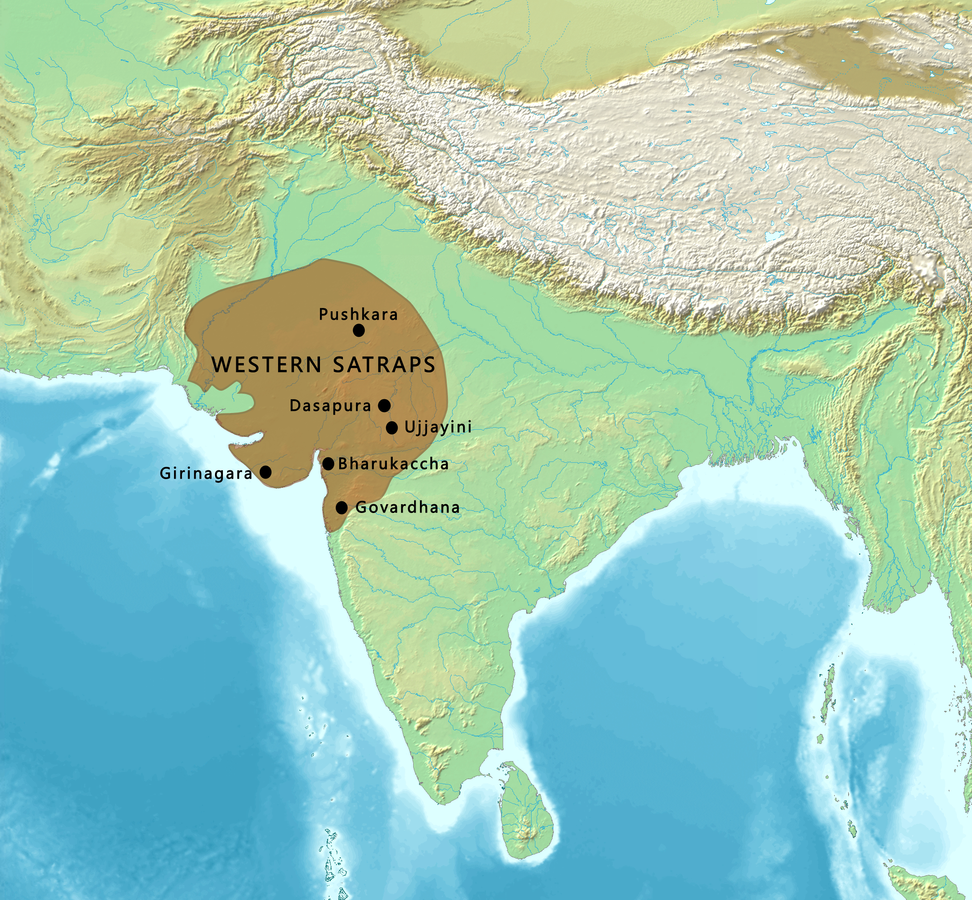
- The Western Satraps was a Saka dynasty which ruled in western India until circa 400 AD
Historiography[edit]
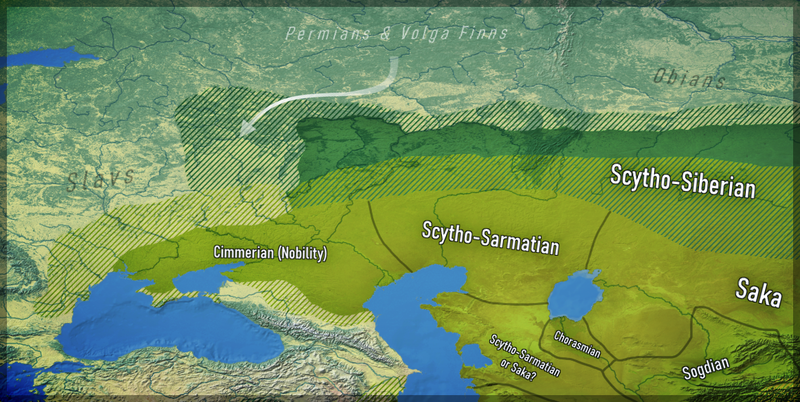
Distribution of Iranic peoples in Central Asia during the Iron Age. Saka included.

Silver coin of the Indo-Scythian King Azes II (ruled c. 35–12 BC). Note the royal tamga on the coin.
Persians referred to all northern nomads as Sakas. Herodotus (IV.64) describes them as Scythians, although they figure under a different name:
The Sacae, or Scyths, were clad in trousers, and had on their heads tall stiff caps rising to a point. They bore the bow of their country and the dagger; besides which they carried the battle-axe, or sagaris. They were in truth Amyrgian (Western) Scythians, but the Persians called them Sacae, since that is the name which they gave to all Scythians.
Strabo[edit]
In the 1st century BC, the Greek-Roman geographer Strabo gave an extensive description of the peoples of the eastern steppe, whom he located in Central Asia beyond Bactria and Sogdiana.[147]
Strabo went on to list the names of the various tribes he believed to be "Scythian",[147] and in so doing almost certainly conflated them with unrelated tribes of eastern Central Asia. These tribes included the Saka.
Now the greater part of the Scythians, beginning at the Caspian Sea, are called Däae, but those who are situated more to the east than these are named Massagetae and Sacae, whereas all the rest are given the general name of Scythians, though each people is given a separate name of its own. They are all for the most part nomads. But the best known of the nomads are those who took away Bactriana from the Greeks, I mean the Asii, Pasiani, Tochari, and Sacarauli, who originally came from the country on the other side of the Iaxartes River that adjoins that of the Sacae and the Sogdiani and was occupied by the Sacae. And as for the Däae, some of them are called Aparni, some Xanthii, and some Pissuri. Now of these the Aparni are situated closest to Hyrcania and the part of the sea that borders on it, but the remainder extend even as far as the country that stretches parallel to Aria. Between them and Hyrcania and Parthia and extending as far as the Arians is a great waterless desert, which they traversed by long marches and then overran Hyrcania, Nesaea, and the plains of the Parthians. And these people agreed to pay tribute, and the tribute was to allow the invaders at certain appointed times to overrun the country and carry off booty. But when the invaders overran their country more than the agreement allowed, war ensued, and in turn their quarrels were composed and new wars were begun. Such is the life of the other nomads also, who are always attacking their neighbors and then in turn settling their differences.
(Strabo, Geography, 11.8.1; transl. 1903 by H. C. Hamilton & W. Falconer.)[147]
IV. 사카인의 언어
Indian sources[edit]
Main article: Indo-Scythians
The Sakas receive numerous mentions in Indian texts, including the Purāṇas, the Manusmṛiti, the Rāmāyaṇa, the Mahābhārata, and the Mahābhāṣya of Patanjali.
Language[edit]
Main article: Saka language
Issyk inscription

Issyk dish with inscription.
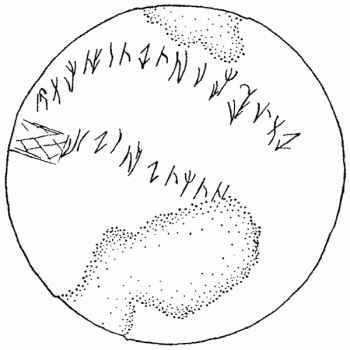
Drawing of the Issyk inscription.
Modern scholarly consensus is that the Eastern Iranian language, ancestral to the Pamir languages in Central Asia and the medieval Saka language of Xinjiang, was one of the Scythian languages.[148] It is unclear whether the Saka spoke a Turkic language or not.[149] Evidence of the Middle Iranian "Scytho-Khotanese" language survives in Northwest China, where Khotanese-Saka-language documents, ranging from medical texts to Buddhist texts, have been found primarily in Khotan and Tumshuq (northeast of Kashgar).[104]
They largely predate the Islamization of Xinjiang under the Turkic-speaking Kara-Khanid Khanate.[104] Similar documents, the Dunhuang manuscripts, were discovered written in the Khotanese Saka language and date mostly from the tenth century.[150]
Attestations of the Saka language show that it was an Eastern Iranian language. The linguistic heartland of Saka was the Kingdom of Khotan, which had two varieties, corresponding to the major settlements at Khotan (now called Hotan) and Tumshuq (now titled Tumxuk).[151][152] Tumshuqese and Khotanese varieties of Saka contain many borrowings from the Middle Indo-Aryan languages, but also share features with the modern Eastern Iranian languages Wakhi and Pashto.[153]
The Issyk inscription, a short fragment on a silver cup found in the Issyk kurgan in Kazakhstan is believed to be the earliest example of Saka, constituting one of very few autochthonous epigraphic traces of that language.[154] The inscription is in a variant of Kharosthi. Harmatta suggests that the inscriptions are a variant of the Kharosthi language, while Christopher Baumer has said that they closely resemble the Old Turkic runic alphabet. From Khotanese Saka, Harmatta translates the inscription as: "The vessel should hold wine of grapes, added cooked food, so much, to the mortal, then added cooked fresh butter on".[155]
Linguistic evidence suggest the Wakhi language is descended from Saka languages.[156][157][158][159] According to the Indo-Europeanist Martin Kümmel, Wakhi may be classified as a Western Saka dialect; the other attested Saka dialects, Khotanese and Tumshuqese, would then be classified as Eastern Saka.[160]
Unterländer, et al. (2017) found genetic evidence that the modern-day descendants of Eastern Scythians are found "almost exclusively" among modern-day Siberian Turkic speakers, suggesting that future studies could determine the extent to which the Eastern Scythians were involved in the early formation of Turkic-speaking populations.[161] According to Tikhonov, et al. (2019), the Eastern Scythians "possibly bore proto-Turkic elements".[162] Another study suggests that this research casts doubt on the historical consensus that the Scythians only spoke an Iranian language.[163]
V. 유전자학으로 본 사카인
Genetics[edit]
See also: Scythian cultures § Genetics, Scythians § Genetics, Sarmatians § Genetics, and Tagar culture § Genetics
The earliest studies could only analyze segments of mtDNA, thus providing only broad correlations of affinity to modern West Eurasian or East Eurasian populations. For example, in a 2002 study the mitochondrial DNA of Saka period male and female skeletal remains from a double inhumation kurgan at the Beral site in Kazakhstan was analysed. The two individuals were found to be not closely related. The HV1 mitochondrial sequence of the male was similar to the Anderson sequence which is most frequent in European populations. The HV1 sequence of the female suggested a greater likelihood of Asian origins.[164]
More recent studies have been able to type for specific mtDNA lineages. For example, a 2004 study examined the HV1 sequence obtained from a male "Scytho-Siberian" at the Kizil site in the Altai Republic. It belonged to the N1a maternal lineage, a geographically West Eurasian lineage.[165] Another study by the same team, again of mtDNA from two Scytho-Siberian skeletons found in the Altai Republic, showed that they had been typical males "of mixed Euro-Mongoloid origin". One of the individuals was found to carry the F2a maternal lineage, and the other the D lineage, both of which are characteristic of East Eurasian populations.[166]

A Saka man from the Pazyryk culture (reconstruction from burials, Anokhin Museum).[167]
These early studies have been elaborated by an increasing number of studies by Russian and western scholars. Conclusions are (i) an early, Bronze Age mixing of both west and east Eurasian lineages, with western lineages being found far to the east, but not vice versa; (ii) an apparent reversal by Iron Age times, with an increasing presence of East Eurasian mtDNA lineages in the Western steppe; (iii) the possible role of migrations from the south, the Balkano-Danubian and Iranian regions, toward the steppe.[168][169]
Haplogroups[edit]
Ancient Y-DNA data was finally provided by Keyser et al in 2009. They studied the haplotypes and haplogroups of 26 ancient human specimens from the Krasnoyarsk area in Siberia dated from between the middle of the 2nd millennium BC and the 4th century AD (Scythian and Sarmatian timeframe). Nearly all subjects belonged to haplogroup R-M17. The authors suggest that their data shows that between the Bronze and the Iron Ages the constellation of populations known variously as Scythians, Andronovians, etc. were blue- (or green-) eyed, fair-skinned and light-haired people who might have played a role in the early development of the Tarim Basin civilisation. Moreover, this study found that they were genetically more closely related to modern populations in eastern Europe than those of central and southern Asia.[170] The ubiquity and dominance of the R1a Y-DNA lineage contrasted markedly with the diversity seen in the mtDNA profiles.
A genetic study published in Nature in May 2018 examined the remains of twenty-eight Inner Asian Sakas buried between ca. 900 BC to AD 1, compromising eight Sakas of southern Siberia (Tagar culture), eight Sakas of the central steppe (Tasmola culture), and twelve Sakas of the Tian Shan. The six samples of Y-DNA extracted from the Tian Shan Saka belonged to the West Eurasian haplogroups R (four samples), R1 and R1a1. For the five central steppe Saka males, four belonged to haplogroup R1a while one individual (DA19) belonged to haplogroup E1b1b-FT167798*.[171]
The samples of mtDNA extracted from the Tian Shan Saka belonged to C4, H4d, T2a1, U5a1d2b, H2a, U5a1a1, HV6 (two samples), D4j8 (two samples), W1c and G2a1.[171]
Autosomal DNA[edit]

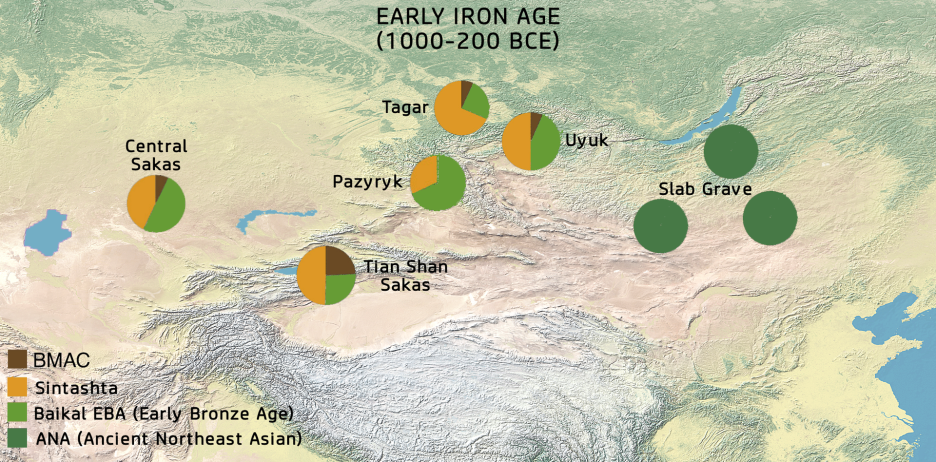
Genetic makeup of Bronze and Iron Age Steppe populations

Map of Scythian cultures, including different Saka populations with genetic profiles, combining Steppe_MLBA, BMAC, and Khövsgöl LBA ancestries.

Genetic makeup of Iron Age Central Asian Scythians. The three main ancestry components are shown in green, red and violet representing the ancestries maximized in Anatolian farmers, Iranian farmers, and Hunter Gatherers from West Siberia, respectively.

Forensic reconstruction of the Saka King and Queen of Arzhan-2, in their burial costumes (650-600 BC).[172]
The 2018 in study detected significant genetic differences between analyzed Inner Asian Saka-associated samples and Scythian samples of the Pannonian Basin, as well as between different Saka subgroups of southern Siberia, the central steppe and the Tian Shan. While Scythians (or "Hungarian Saka") harbored exclusively ancestry associated with Western Steppe Herders, Inner Asian Saka displayed additional Neolithic Iranian (BMAC) and Southern Siberian hunter-gatherer (represented through a proxy of modern Altaians) components in varying degrees. Tian Shan Sakas were found to be of about 70% Western Steppe Herder (WSH) ancestry, 25% Southern Siberian Hunter-Gatherer ancestry and 5% Iranian Neolithic ancestry. The Iranian Neolithic ancestry was probably from the Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex. Sakas of the Tasmola culture were found to be of about 56% WSH ancestry and 44% Southern Siberian Hunter-Gather ancestry. The peoples of the Tagar culture had about 83.5% WSH ancestry, 9% Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) ancestry and 7.5% Southern Siberian Hunter-Gatherer ancestry. The study suggested that the Inner Asian Saka were the source of West Eurasian ancestry among the Xiongnu, and that the Huns probably emerged through minor male-driven geneflow into the Saka through westward migrations by the Xiongnu.[173] A genetic study published in 2020 in Cell,[174] modeled the ancestry of several Saka groups as a combination of Sintashta (Western Steppe Herders) and Baikal EBA ancestry (Western Baikal early Bronze Age hunter-gatherers, a profile consisting of about 80% Ancient Northeast Asian and 20% Ancient North Eurasian ancestries),[175] with varying degrees of an additional Neolithic Iranian (BMAC) component.[174] Specifically, Central Sakas of the Tasmola culture were found to be of about 43% Sintashta ancestry, 50% Baikal_EBA ancestry and 7% BMAC ancestry. Tagar Sakas (Tagar culture) were found to have an elevated Sintashta proportion (69% Sintashta, 24% Baikal_EBA, and 7% BMAC), while Tian Shan Sakas had an elevated BMAC proportion at 24% (50% Sintashta, 26% Baikal_EBA, and 24% BMAC). The eastern Uyuk Sakas (Arzhan culture) had 50% Sintashta, 44% Baikal_EBA, and 6% BMAC ancestry. The Pazyryk Sakas had elevated Baikal_EBA ancestry, with a nearly non-existent BMAC component (32% Sintashta, 68% Baikal_EBA, and ~0% BMAC).[176] Two other genetic studies published in 2021 and 2022 found that the Saka originated from a shared WSH-like (Srubnaya, Sintashta, and Andronovo culture) background with additional BMAC and East Eurasian-like ancestry. The Eastern ancestry among the Saka can also be represented by Lake Baikal (Shamanka_EBA-like) groups. The spread of Saka-like ancestry can be linked with the dispersal of Eastern Iranian languages (such as Khotanese).[177][178]
A later different Eastern influx is evident in three outlier samples of the Tasmola culture (Tasmola Birlik) and one of the Pazyryk culture (Pazyryk Berel), which displayed c. 70-83% additional Ancient Northeast Asian ancestry represented by the Neolithic Devil’s Gate Cave specimen, suggesting them to be recent migrants from further East. The same additional Eastern ancestry is found among the later groups of Huns (Hun Berel 300CE, Hun elite 350CE), and the Karakaba remains (830CE). At the same time, western Sarmatian-like and minor additional BMAC-like ancestry spread eastwards, with a Saka-associated sample from southeastern Kazakhstan (Konyr Tobe 300CE) displaying around 85% Sarmatian and 15% BMAC ancestry. Sarmatians are modeled to derive primarily from the preceding Western Steppe Herders of the Pontic–Caspian steppe.[179]

The Sakas represent a unique period of West-East admixture along the Altai line during the Iron Age, which has been a defining characteristic of Central Asian populations until modern times.[180]
The most closely related modern population to the Saka (and other Scythian groups) are the Tajiks, an Iranian peoples indigenous to Southern Central Asia, which display genetic continuity to Bronze and Iron age Central Asians. These genetic links are paralleled by previous proposed "linguistic and physical anthropological links between the Tajiks and Scythians".[181] There is also increasing evidence for genetic continuity from the Eastern Scythians (such as the Pazyryk culture) to later Turkic-speaking peoples,[182] which formed via admixture events during the Iron Age between local Saka groups and geneflow from the Eastern Steppe.[183] The admixture with West Eurasian sources was found to be "in accordance with the linguistically documented language borrowing in Turkic languages".[184]
East-West migrations and cultural transmission[edit]
Genetic data across Eurasia suggest that the Scythian cultural phenomenon was accompanied by some degree of migration from east to west, starting in the area of the Altai region.[185] In particular, the Classical Scythians of the western Eurasian steppe were not direct descendants of the local Bronze Age populations, but partly resulted from this east-west spread.[185] This also suggests that Scythoïd cultural characteristics were not simply the result of the transfer of material culture, but were also accompanied by human migrations of Saka populations from the east.[185]
The region between the Caspian Sea and of the Southern Urals originally had populations of Srubnaya (1900 BC–1200 BCE) and Andronovo (c. 2000–1150 BCE) ancestry ancestry, but, starting with the Iron Age (c.1000 BCE) became a region of intense ethnic and cultural interraction between European and Asian components.[186] From the 7th century BCE, Early Saka nomads started to settle in the Southern Urals, coming from Central Asia, the Altai-Sayan region, and Central and Northern Kazakhstan.[186] The Itkul culture (7th-5th century BCE) is one of these Early Saka cultures, based in the eastern foothills of the Urals, which was assimilited into the Sauromatian and Early Sarmatian cultures.[186] Circa 600 BCE, groups from the Saka Tasmola culture settled in the southern Urals.[186] Circa 500 BCE, other groups from the area of Ancient Khorezm settled in the western part of the southern Urals, who also assimilated into the Early Sarmatians.[186] As a result, a large-scale integrated union of nomads from Central Asia formed in the area in the 5th–4th century BCE, with fairly uniformized cultural practices.[186] This cultural complex, with notable ‘‘foreign elements’’, corresponds to the ‘‘royal’’ burials of Filippovka kurgan, and define the "Prokhorovka period" of the Early Sarmatians.[186]

- Warriors with daggers and bows. Dagger blade decoration from Kurgan 4, Burial 2, Filippovka kurgans, Late Sauromatian-Early Sarmatian, 5th-4th century BCE.[187]

- "Golden Lady " from the Taksai kurgans, c. 500 BCE.[188][189]
VII. 사카의 고고학적 유믈
Archaeology[edit]
|
Saka kurgans[190]
|
|
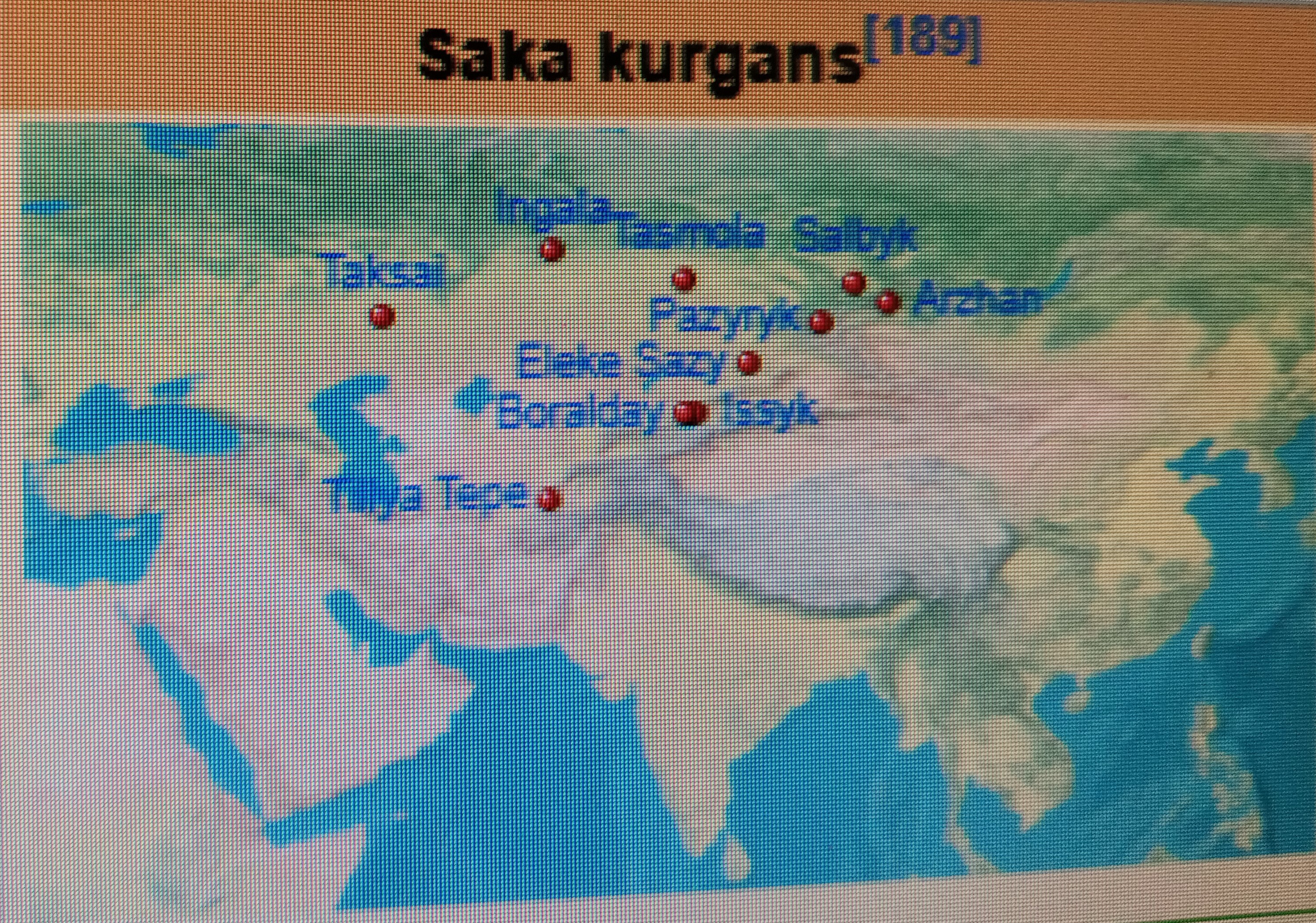 Salbyk Arzhan Pazyryk Issyk Boralday Taksai Eleke Sazy Tasmola Ingala Tillya Tepe |
|
|
Arzhan-1
|
c. 800 BCE
|
|
Shilikty
|
c. 700 BCE
|
|
Arzhan-2
|
c. 650 BCE
|
|
Bes Shatyr
|
c. 550 BCE
|
|
Taksai
|
c. 500 BCE
|
|
Ingala
|
c. 500 BCE
|
|
Tasmola
|
7th-5th centuries BCE
|
|
Boralday
|
c. 600-400 BCE
|
|
Salbyk
|
c. 600-400 BCE
|
|
Eleke Sazy
|
c. 600-400 BCE
|
|
Berel-1
|
c. 350 BCE
|
|
Pazyryk-1,2
|
c. 300 BCE
|
|
Berel-11
|
c. 300 BCE
|
|
Issyk
|
c. 400-200 BCE
|
|
Tillya Tepe
|
1st century BCE
|
|
|

Compative timeline of Scythian kurgans in Asia and Europe.[191]
The spectacular grave-goods from Arzhan, and others in Tuva, have been dated from about 800 BC onward, and the kurgans of Shilikty in eastern Kazakhstan circa 700 BC, and are associated with the Early Sakas.[192] Burials at Pazyryk in the Altay Mountains have included some spectacularly preserved Sakas of the "Pazyryk culture" – including the Ice Maiden of the 5th century BC.
1. Arzhan 1 kurgan (c. 800 BC)[edit]
Main article: Arzhan culture
Arzhan-1 was excavated by M. P. Gryaznov in the 1970s, establishing the origins of Scythian culture in the region in the 10th to 8th centuries BC:[193] Arzhan-1 was carbon-dated to circa 800 BC.[194] Many of the styles of the artifacts found in Arzhan 1 (such as the animal style images of deer, boar, and panther) soon propagated to the west, probably following a migration mouvement from the east to the west in the 9th-7th centuries BC, and ultimately reaching European Scythia and influencing artistic styles there.[195]
- Arzhan-1, dated to circa 800 BC, partly looted in Antiquity

- Curled-up feline animal from Arzhan-1, circa 800 BC.[196]
2. Shilikty/ Baigetobe kurgan (c. 700 BC)[edit]
Main article: Shilikty
Shilikty is an archaeological site in eastern Kazakhstan with numerous 8th-6th century BC Early Saka kurgans.[197][198] Carbon-14 dating suggests date of 730-690 BC for the kurgans, and a broad contemporaneity with the Arzhan-2 kurgan in Tuva.[197]
The Kurgans contained vast quantities of precious golden jewelry.[199] Remains of a "golden man" (similar to the Issyk kurgan golden man) were found in 2003, with 4262 gold finds.[200]
3. Arzhan 2 (c. 650 BC)[edit]
See also: Aldy-Bel culture

Arzhan 2 kurgan (7th-6th centuries BC, associated with the Aldy-Bel culture).[201]
Arzhan-2 was an undisturbed burial.[202] Archaeologists found a royal couple, sixteen murdered attendants, and 9,300 objects.[202] 5,700 of these artifacts were made of gold, weighing a Siberian record-breaking twenty kilograms.[202] The male, who researchers guess was some sort of king, wore a golden torc, a jacket decorated with 2,500 golden panther figurines, a gold-encrusted dagger on a belt, trousers sewn with golden beads, and gold-cuffed boots.[202] The woman wore a red cloak that was also covered in 2,500 golden panther figurines, as well as a golden-hilted iron dagger, a gold comb, and a wooden ladle with a golden handle.[202]
- "Animal style" deer, (7-6th century BC) Tuva.
- Pectoral plate, from burial mound Arzhan (7-6th century BC) Tuva.
- Akinak (dagger) burial mound Arzhan (7-6th century BC) Tuva.
4. Eleke Sazy Burial Complex (c. 800-400 BC)[edit]

Recumbent stag plaque, Eleke Sazy, Kazakhstan; 8th to 6th century BC
In 2020, archaeologists excavated multiple burial mounds in the Eleke Sazy Valley in East Kazakhstan. Here, a large number of gold artifacts were found. These artifacts included golf harness fittings, pendants, chains, appliqués, and more – most of which are in the Animal Style of the Scythian-Saka era dating back to the 5th–4th centuries BC.[203]
5. Berel burial mound (c. 350-300 BC)[edit]
Near the selo of Berel in the Katonkaragay District of eastern Kazakhstan (49°22′24″N 86°26′17″E[204]) excavations of ancient burial mounds have revealed artefacts the sophistication of which are encouraging a revaluation of the nomadic cultures of the 3rd and 4th centuries BC.[205]
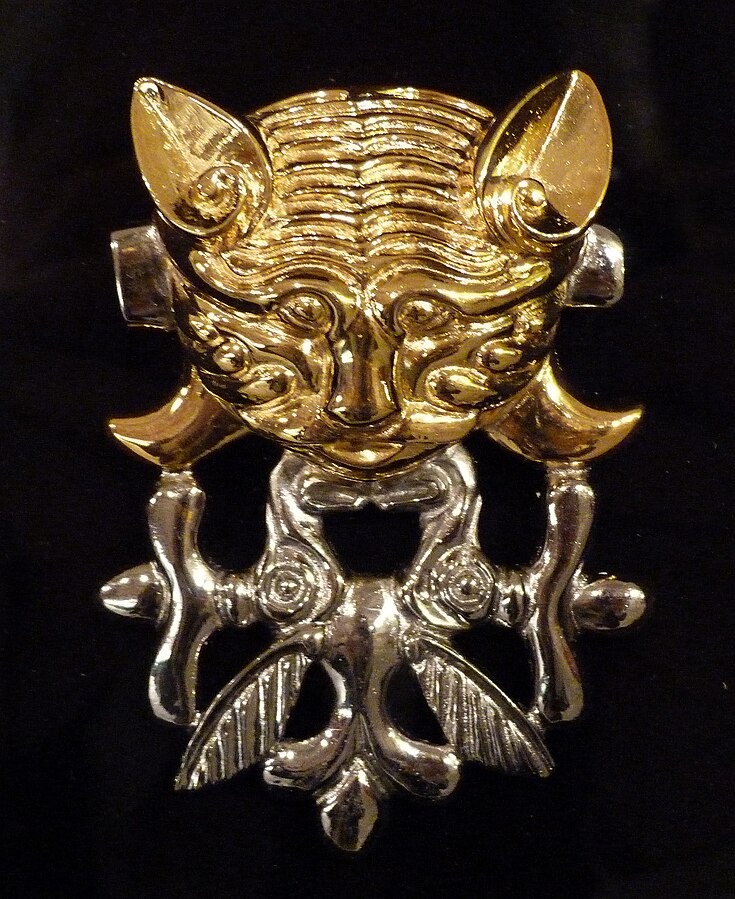

- Catlike predator with protomas of two elk, burial mound Berel (4th-3rd centuries BC) Kazakhstan, Pazyryk culture.
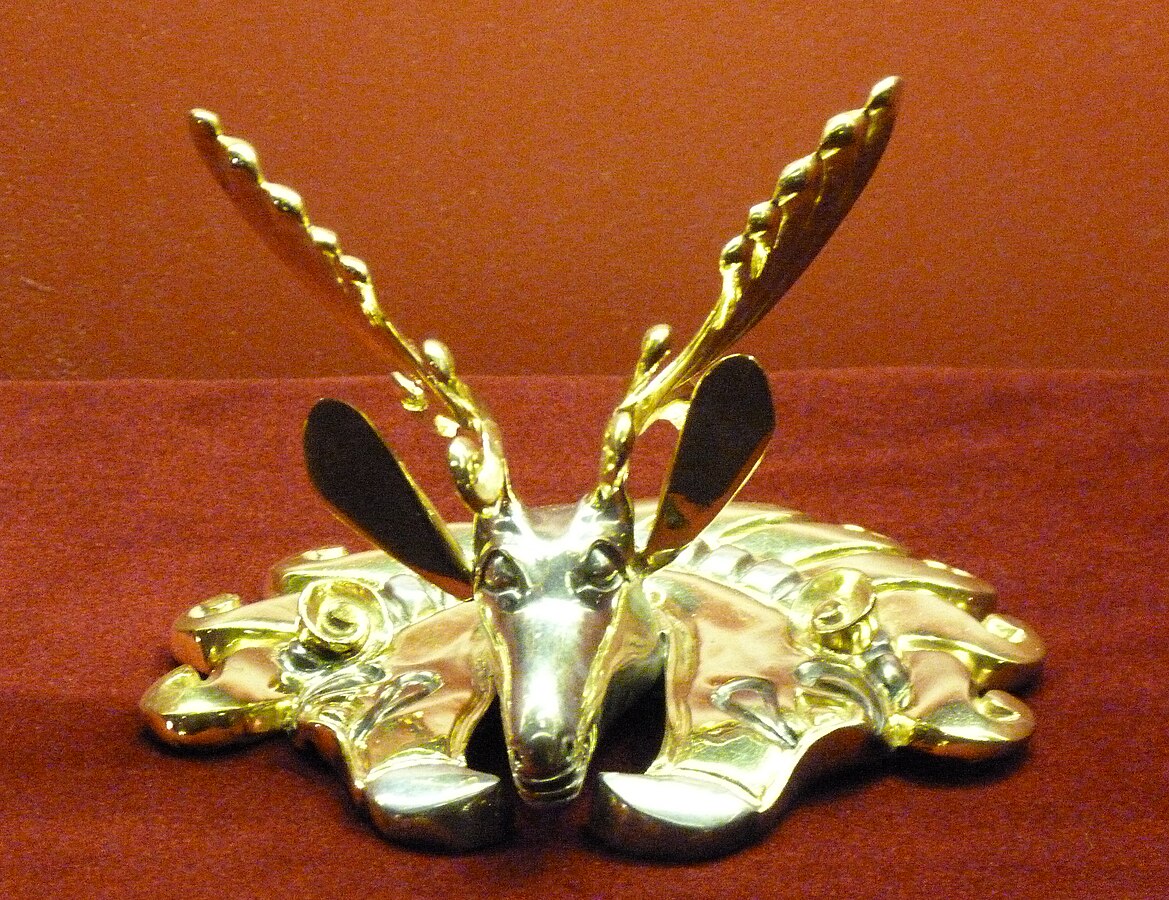

- Deer in Griffin's beak, burial mound Berel (4th-3rd centuries BC) Kazakhstan.
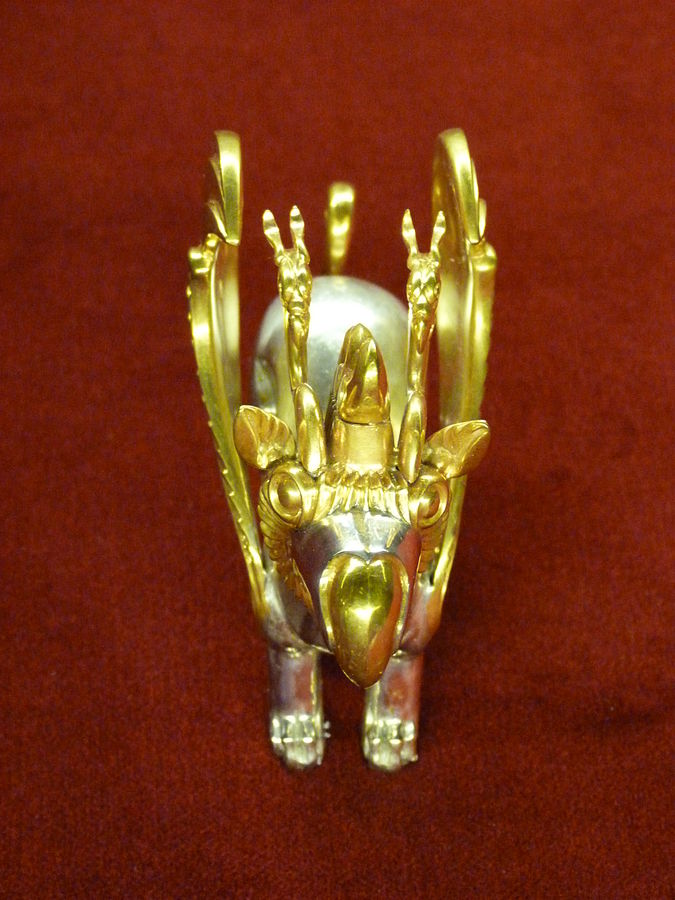

- Tigergriffin arthor work based on Scytian- saka animal style, burial mound Berel (5th-3rd centuries BC) Kazakhstan.
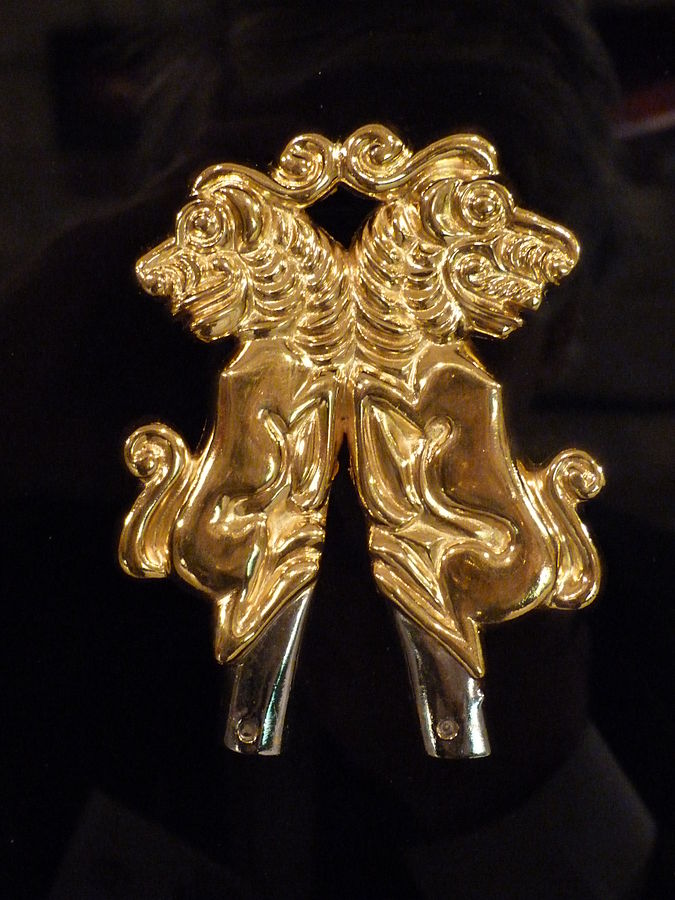

- Griffins, burial mound Berel (5th-3rd centuries BC) Kazakhstan.

- Frontal decoration (harness), burial mound Berel (4th-3rd centuries BC) Kazakhstan, Pazyryk culture.
6. Pazyryk culture (c. 300 BC)[edit]
Main article: Pazyryk culture

A Pazyryk horseman in a felt painting from a burial around 300 BC. The Pazyryks appear to be closely related to the Scythians.[206]
Saka burials documented by modern archaeologists include the kurgans at Pazyryk in the Ulagan (Red) district of the Altai Republic, south of Novosibirsk in the Altai Mountains of southern Siberia (near Mongolia).
Archaeologists have extrapolated the Pazyryk culture from these finds: five large burial mounds and several smaller ones between 1925 and 1949, one opened in 1947 by Russian archaeologist Sergei Rudenko. The burial mounds concealed chambers of larch-logs covered over with large cairns of boulders and stones.[207]
The Pazyryk culture flourished between the 7th and 3rd century BC in the area associated with the Sacae.
Ordinary Pazyryk graves contain only common utensils, but in one, among other treasures, archaeologists found the famous Pazyryk Carpet, the oldest surviving wool-pile oriental rug. Another striking find, a 3-metre-high four-wheel funerary chariot, survived well-preserved from the 5th to 4th century BC.[208]
7. Southern Siberian kurgans excavated in the 18th century[edit]
Main article: Siberian Collection of Peter the Great
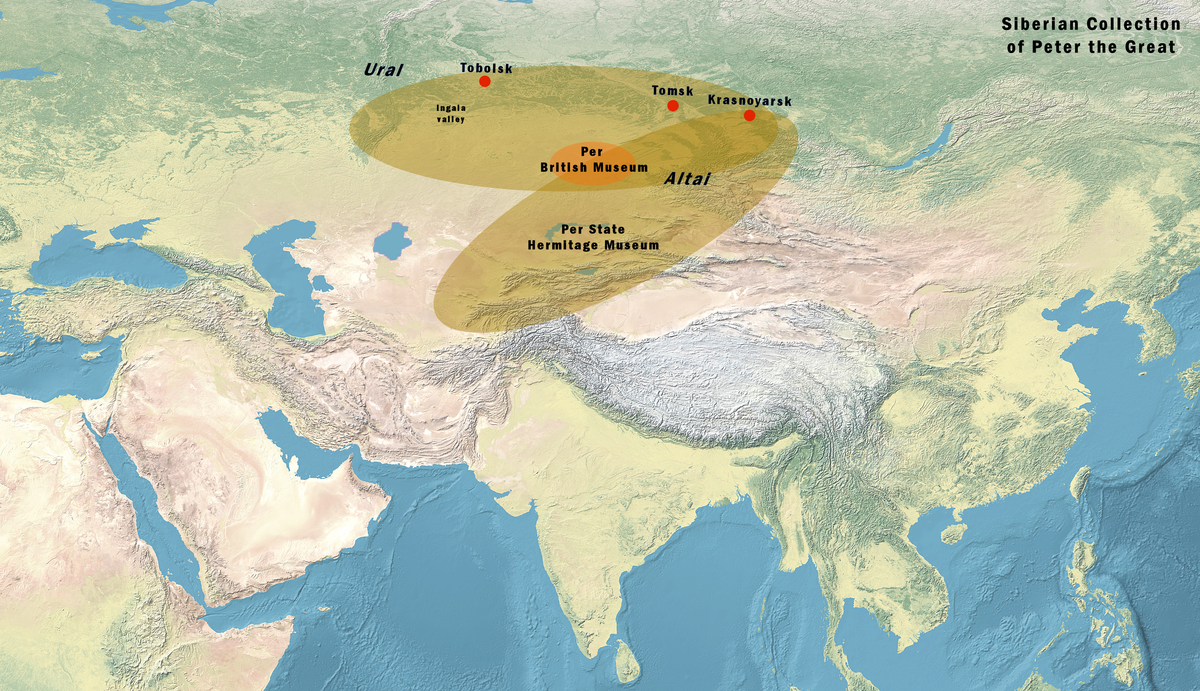
Approximate location of the finds of the Siberian Collection of Peter the Great.[209][210]
During the 18th century and the Rusian expansion into Siberia, many Saka kurgans were plundered, sometimes by independent grave-robbers or sometimes officially at the instigation of Peter the Great, but usually without any archaeological records being taken.[211] Only the general location where they were excavated is known, between modern Kazakhstan and the Altai mountains.[209]
Many of these artifacts were part of the archaeological presents sent by Matvey Gagarin [ru], Governor of Siberia based in Tobolsk, to Peter the Great in Saint-Petersburg in 1716.[212] They are now located in the Hermitage Museum in Saint-Petersburg, and form the Siberian Collection of Peter the Great. Their estimated datation ranges from the 7th century BC to the 1st century BC, depending on the artifacts.[209]
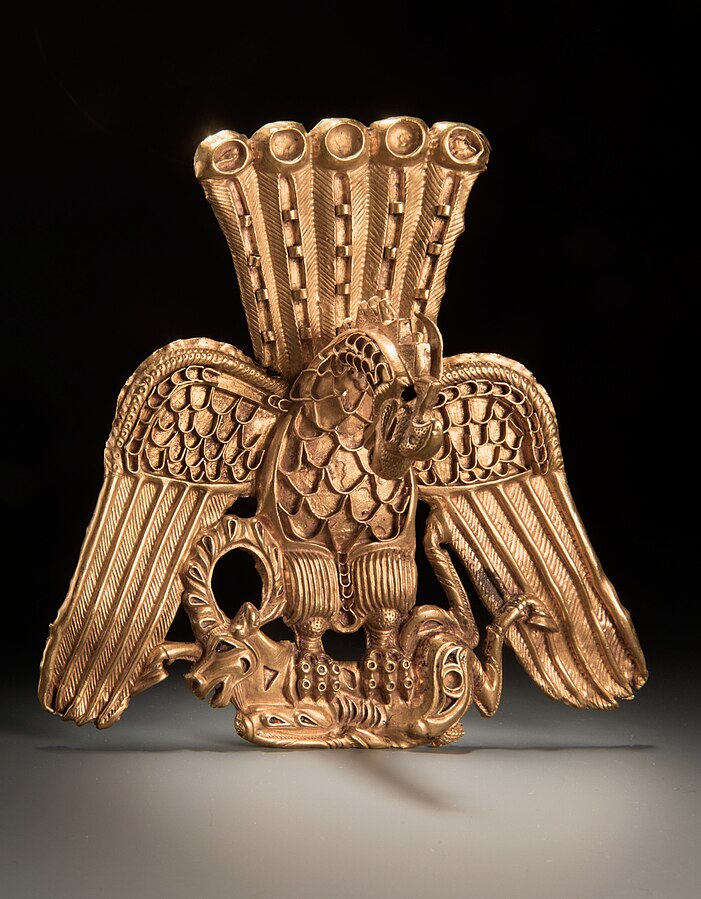

- Aigrette, 4th-3rd century BC. Siberian Collection of Peter the Great.[213]

- Boar hunter (Hermitage Museum), 2nd-1st century BC.[214]

- Belt plaque from the Siberian collection of Peter the Great, probably Ingala Valley

- Siberian gold, Siberian Collection of Peter the Great
8. Tillia Tepe treasure (2nd-1st century BC)[edit]
Main article: Tillia Tepe

Artifacts found the tombs 2 and 4 of Tillya Tepe and reconstitution of their use on the man and woman found in these tombs
A site found in 1968 in Tillia Tepe (literally "the golden hill") in northern Afghanistan (former Bactria) near Shebergan consisted of the graves of five women and one man with extremely rich jewelry, dated to around the 1st century BC, and probably related to that of Saka tribes normally living slightly to the north.[215] Altogether the graves yielded several thousands of pieces of fine jewelry, usually made from combinations of gold, turquoise and lapis-lazuli.
A high degree of cultural syncretism pervades the findings, however. Hellenistic cultural and artistic influences appear in many of the forms and human depictions (from amorini to rings with the depiction of Athena and her name inscribed in Greek), attributable to the existence of the Seleucid empire and Greco-Bactrian kingdom in the same area until around 140 BC, and the continued existence of the Indo-Greek kingdom in the northwestern Indian sub-continent until the beginning of our era. This testifies to the richness of cultural influences in the area of Bactria at that time.
VIII. 사카 문화
Culture[edit]
Gender roles[edit]
Recently, evidence confirmed by the full-genomic analysis of a Scythian child's remains found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, which was discovered in Saryg-Bulun in Central Tuva, revealed that the individual, previously thought to be male because it had items that were associated with the belief that Scythian society was male-dominated, was actually female. Along with the leather skirt, the burial also contained a leather headdress painted with red pigment, a coat sewn from jerboa fur, a leather belt with bronze ornaments and buckles, a leather quiver with arrows with painted ornaments on the shafts, a fully-preserved battle pick, and a bow. These items provide valuable insights into the material culture and lifestyle of the Scythians, including their hunting and warfare practices, and their use of animal hides for clothing.[216]
Art[edit]
Further information: Scythian art

Battle scenes between "Kangju" Saka warriors, from the Orlat plaques. 1st century AD.
The art of the Saka was of a similar styles as other Iranian peoples of the steppes, which is referred to collectively as Scythian art. In 2001, the discovery of an undisturbed royal Scythian burial-barrow at Arzhan illustrated Scythian animal-style gold that lacks the direct influence of Greek styles. Forty-four pounds of gold weighed down the royal couple in this burial, discovered near Kyzyl, capital of the Siberian republic of Tuva.
Ancient influences from Central Asia became identifiable in China following contacts of metropolitan China with nomadic western and northwestern border territories from the 8th century BC. The Chinese adopted the Scythian-style animal art of the steppes (descriptions of animals locked in combat), particularly the rectangular belt-plaques made of gold or bronze, and created their own versions in jade and steatite.[217]
Following their expulsion by the Yuezhi, some Saka may also have migrated to the area of Yunnan in southern China. Saka warriors could also have served as mercenaries for the various kingdoms of ancient China. Excavations of the prehistoric art of the Dian civilisation of Yunnan have revealed hunting scenes of Caucasoid horsemen in Central Asian clothing.[218]
Saka influences have been identified as far as Korea and Japan. Various Korean artifacts, such as the royal crowns of the kingdom of Silla, are said to be of "Scythian" design.[219] Similar crowns, brought through contacts with the continent, can also be found in Kofun era Japan.[220]
Clothing[edit]

Saka-style Majiayuan culture tomb figurines (3rd-2nd century BC).[221]
Similar to other eastern Iranian peoples represented on the reliefs of the Apadana at Persepolis, Sakas are depicted as wearing long trousers, which cover the uppers of their boots. Over their shoulders they trail a type of long mantle, with one diagonal edge in back. One particular tribe of Sakas (the Saka tigraxaudā) wore pointed caps. Herodotus in his description of the Persian army mentions the Sakas as wearing trousers and tall pointed caps.[222]

Statuette from the Saka culture in Xinjiang, from a 3rd-century BC burial site north of the Tian Shan, Xinjiang Region Museum, Ürümqi.[223][224] Could alternatively be a Greek hoplite.[225]
Men and women wore long trousers, often adorned with metal plaques and often embroidered or adorned with felt appliqués; trousers could have been wider or tight fitting depending on the area. Materials used depended on the wealth, climate and necessity.[226]
Herodotus says Sakas had "high caps tapering to a point and stiffly upright." Asian Saka headgear is clearly visible on the Persepolis Apadana staircase bas-relief – high pointed hat with flaps over ears and the nape of the neck.[227] From China to the Danube delta, men seemed to have worn a variety of soft headgear – either conical like the one described by Herodotus, or rounder, more like a Phrygian cap.
Saka women dressed in much the same fashion as men. A Pazyryk burial, discovered in the 1990s, contained the skeletons of a man and a woman, each with weapons, arrowheads, and an axe. Herodotus mentioned that Sakas had "high caps and … wore trousers." Clothing was sewn from plain-weave wool, hemp cloth, silk fabrics, felt, leather and hides.

The Taerpo horserider, a Chinese Warrior-State Qin terracotta figurine from a tomb in the Taerpo cemetery near Xianyang in Shaanxi Province, 4th-3rd century BC. This is the earliest known representation of a cavalryman in China.[228] The outfit is of Central Asian style, probably Scythian,[229] and the rider with his high-pointed nose appears to be a foreigner.[228] King Zheng of Qin (246–221 BC) is known to have employed steppe cavalry men in his army, as seen in his terracotta army.[230]
Pazyryk findings give the most almost fully preserved garments and clothing worn by the Scythian/Saka peoples. Ancient Persian bas-reliefs, inscriptions from Apadana and Behistun and archaeological findings give visual representations of these garments.
Based on the Pazyryk findings (can be seen also in the south Siberian, Uralic and Kazakhstan rock drawings) some caps were topped with zoomorphic wooden sculptures firmly attached to a cap and forming an integral part of the headgear, similar to the surviving nomad helmets from northern China. Men and warrior women wore tunics, often embroidered, adorned with felt applique work, or metal (golden) plaques.
Persepolis Apadana again serves a good starting point to observe the tunics of the Sakas. They appear to be a sewn, long-sleeved garment that extended to the knees and was girded with a belt, while the owner's weapons were fastened to the belt (sword or dagger, gorytos, battle-axe, whetstone etc.). Based on numerous archeological findings, men and warrior women wore long-sleeved tunics that were always belted, often with richly ornamented belts. The Kazakhstan Saka (e.g. Issyk Golden Man/Maiden) wore shorter and closer-fitting tunics than the Pontic steppe Scythians. Some Pazyryk culture Saka wore short belted tunic with a lapel on the right side, with upright collar, 'puffed' sleeves narrowing at the wrist and bound in narrow cuffs of a color different from the rest of the tunic.
Men and women wore coats: e.g. Pazyryk Saka had many varieties, from fur to felt. They could have worn a riding coat that later was known as a Median robe or Kantus. Long sleeved, and open, it seems that on the Persepolis Apadana Skudrian delegation is perhaps shown wearing such coat. The Pazyryk felt tapestry shows a rider wearing a billowing cloak.
Tattoos[edit]
Men and women are known to have been extensively tattooed. The men in the Pazyryk burials had extensive tattoes in the Siberian animal style.[231] A Pazyryk chief in burial mound 2, had his body covered in animal style tattoos, but not his face.[232] Parts of the body had deteriorated, but much of the tattooing was still clearly visible (see image). Subsequent investigation using reflected infrared photography revealed that all five bodies discovered in the Pazyryk kurgans were tattooed.[233] No instruments specifically designed for tattooing were found, but the Pazyryks had extremely fine needles with which they did miniature embroidery, and these were probably used for tattooing. The chief was elaborately decorated with an interlocking series of striking designs representing a variety of fantastic beasts. The best preserved tattoos were images of a donkey, a mountain ram, two highly stylized deer with long antlers and an imaginary carnivore on the right arm. Two monsters resembling griffins decorate the chest, and on the left arm are three partially obliterated images which seem to represent two deer and a mountain goat. On the front of the right leg a fish extends from the foot to the knee. A monster crawls over the right foot, and on the inside of the shin is a series of four running rams which touch each other to form a single design. The left leg also bears tattoos, but these designs could not be clearly distinguished. In addition, the chief's back was tattooed with a series of small circles in line with the vertebral column.[234] The Siberian Ice Maiden is also known for her extensive tattoes.[235]

- Tattoos of the Pazyryk-2 chief.[236]

- Tattoos of the chief's right arm, with zoomorphic symbols.[235]

- Tattoos of the chief's back and left arm.[235]
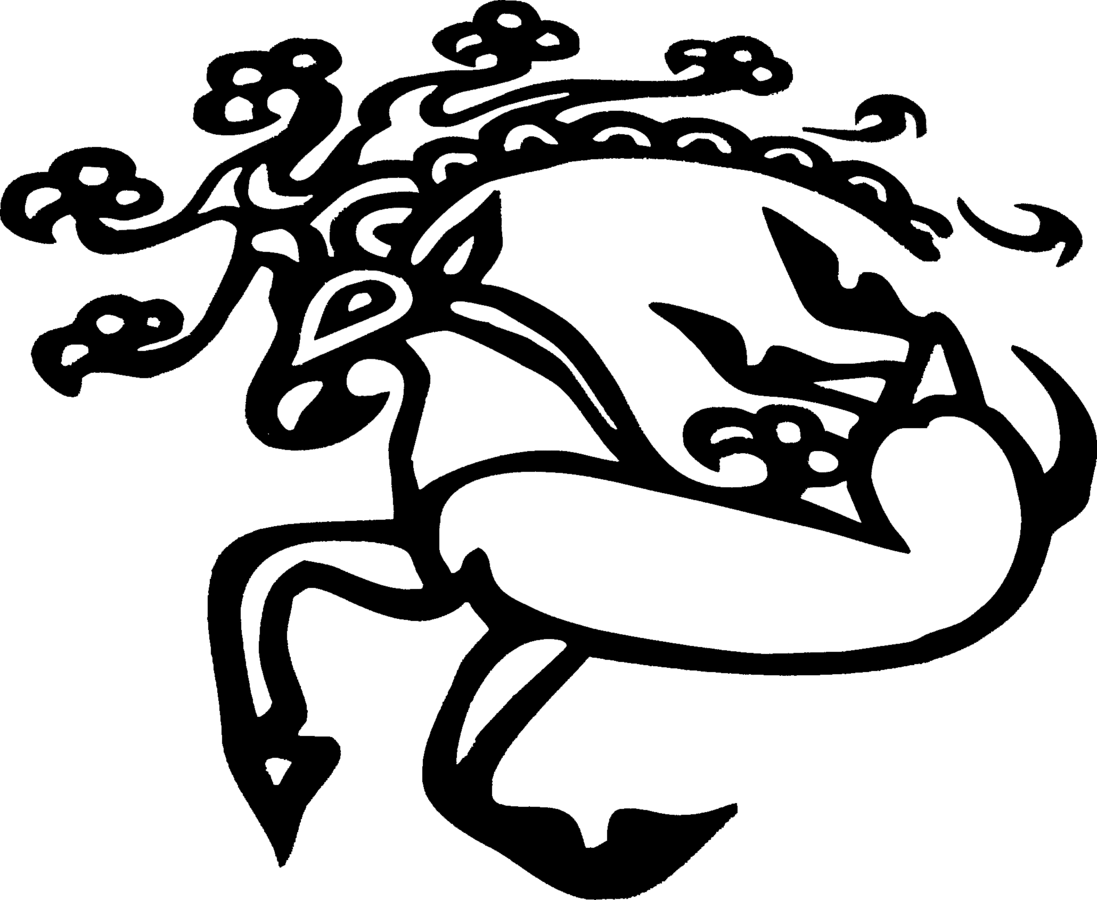

- Tattoo motif on the arm of the Siberian Ice Maiden.[235]
Warfare[edit]
A skull from an Iron Age cemetery in South Siberia shows evidence of scalping. It lends physical evidence to the practice of scalp taking by the Scythians living there.[237]
Later depictions of "Sakas" in China (1st-3rd century AD)[edit]
Numerous depictions of foreigners of Saka appearance appear in China around the Eastern Han period (25–220 AD), sometimes as far as east as Shandong. They may have appeared in relation with the conflicts against the Scythoïd Xirong in the west or the Donghu people in the North, or the Kushans in the area of Xinjiang. They were generally called "Hu" by the Chinese.[238][239][240]

- Mingqi (Chinese funerary statuette) of a young Central Asian man, with Saka-type caftan and conical hat reminiscent of early 3rd century AD Kushans. Later Han, 3rd century AD. Guimet Museum (MA 4660).[238]

- Eastern Han tombs sometimes have depiction of battles between Hu barbarians, with bows and arrows and wearing pointed hats (left), against Han troops. Eastern Han Dynasty (151–153 AD). Tsangshan Han tomb in Linyi city. Also visible in Yinan tombs.[240]

- General appearance of the numerous Scythoïd Hu monumental statues from Shandong, featuring people with a high nose, deep eyes and a pointed hat. Eastern Han period.[239]

- Yinan tombs relief, depicting an attack by Hu barbarians with pointed hats, bow and arrows. 2nd century AD, Eastern Han.[241]
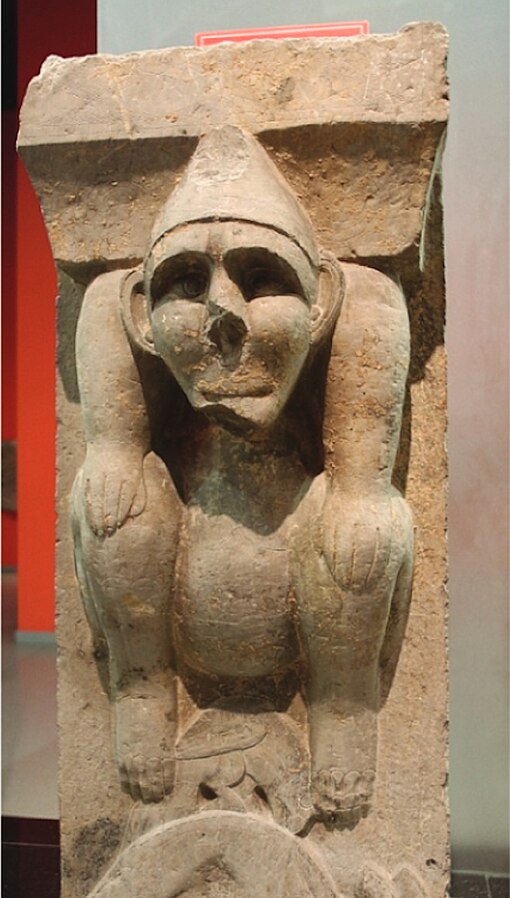

- Hu statue from Wu Baizhuang tomb (吳白莊), Han dynasty period, Linyi, Shandong.[242]

- Hu statue from Wu Baizhuang tomb (吳白莊), Han dynasty period, Linyi, Shandong.[242]

- Man hunting, circa 500 BC, Gansu Museum.[243]
IV. Saka 이전의 문명
1. Andronov culture (2000-1150 BC)

Andronovo culture area
The Andronovo culture[a] is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished c. 2000–1150 BC,[1][2][3][4] spanning from the southern Urals to the upper Yenisei River in central Siberia.[5][6] Some researchers have preferred to term it an archaeological complex or archaeological horizon.[7] The slightly older Sintashta culture (c. 2200–1900 BC), formerly included within the Andronovo culture, is now considered separately to Early Andronovo cultures.[8][9] Andronovo culture's first stage could have begun at the end of the 3rd millennium BC, with cattle grazing, as natural fodder was by no means difficult to find in the pastures close to dwellings.[10][11][12]
Most researchers associate the Andronovo horizon with early Indo-Iranian languages, though it may have overlapped the early Uralic-speaking area at its northern fringe.[13] Allentoft et al. (2015) concluded from their genetic studies that the Andronovo culture and the preceding Sintashta culture should be partially derived from the Corded Ware culture, given the higher proportion of ancestry matching the earlier farmers of Europe, similar to the admixture found in the genomes of the Corded Ware population.[14]
Discovery[edit]
The name derives from the village of Andronovo in the Uzhursky District of Kranoyarsk Krai, Siberia, where the Russian zoologist Arkadi Tugarinov discovered its first remains in 1914. Several graves were discovered, with skeletons in crouched positions, buried with richly decorated pottery. The Andronovo culture was first identified by the Russian archaeologist Sergei Teploukhov in the 1920s.[15]
Dating and subcultures[edit]

Archaeological cultures associated with Indo-Iranian migrations (after EIEC): The Andronovo, BMAC and Yaz cultures have often been associated with Indo-Iranian migrations. The Gandhara grave (or Swat), Cemetery H, Copper Hoard and Painted Grey Ware cultures are candidates for the Indo-Aryan migration into South Asia.
The culture of Sarazm (4th–3rd millennium BC) precedes the arrival of the Andronovo steppe culture in South Central Asia in the 2nd millennium BC.[16][17][18]
Currently only two sub-cultures are considered as part of Andronovo culture:[2]
- Alakul (2000–1700 BC)[3] between Oxus (today Amu Darya), and Jaxartes (today Syr Darya), Kyzylkum desert
- Fëdorovo (2000–1450 BC)[19][3] in southern Siberia (earliest evidence of cremation and fire cult[20])
Other authors identified previously the following sub-cultures also as part of Andronovo:
- Eastern Fedorovo (1850–1350 BC)[21][22] in Tian Shan mountains (Northwestern Xinjiang, China), southeastern Kazakhstan, eastern Kyrgyzstan
- Alekseyevka-Sargary (1450–1150 BC)[4][23] "final Bronze Age phase" in eastern Kazakhstan, contacts with Namazga VI in Turkmenia, Ingala Valley in the south of Tyumen Oblast, in Tobol.
Some authors have challenged the chronology and model of eastward spread due to increasing evidence for the earlier presence of these cultural features in parts of east Central Asia.[24]
Geographic extent[edit]
The geographical extent of the culture is vast and difficult to delineate exactly. On its western fringes, it overlaps with the approximately contemporaneous, but distinct, Srubna culture in the Volga-Ural interfluvial. To the east, it reaches into the Minusinsk depression, with some sites as far west as the southern Ural Mountains,[25] overlapping with the area of the earlier Afanasevo culture.[26] Additional sites are scattered as far south as the Koppet Dag (Turkmenistan), the Pamir (Tajikistan) and the Tian Shan (Kyrgyzstan). The northern boundary vaguely corresponds to the beginning of the Taiga.[25] More recently, evidence for the presence of the culture in Xinjiang in far-western China has also been found,[24] mainly concentrated in the area comprising Tashkurgan, Ili, Bortala, and Tacheng area.[27] In the Volga basin, interaction with the Srubna culture was the most intense and prolonged, and Federovo style pottery is found as far west as Volgograd. Mallory notes that the Tazabagyab culture south of Andronovo could be an offshoot of the former (or Srubna), alternatively the result of an amalgamation of steppe cultures and the Central Asian oasis cultures (Bishkent culture and Vakhsh culture).[6]
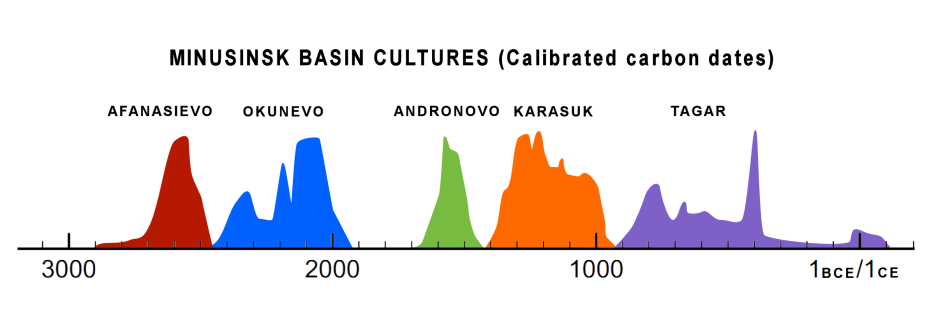
Dates of Minusinsk Basin cultures, at the easternmost edge of Adronovo culture (Summed probability distribution for new human bone dates, Afanasievo to Tagar cultures).[28]
In the initial Sintashta-Petrovka phase,[27] the Andronovo culture is limited to the northern and western steppes in the southern Urals-Kazakhstan.[6] Since then, at the 2nd millennium, in the Alakul Phase (2000–1700 BC),[3] the Fedorovo Phase (1850–1450 BC)[3] and the final Alekseyevka Phase (1400–1000 BC), the Andronovo cultures move intensively eastwards, expanding as far east as the Upper Yenisei River, succeeding the non-Indo-European Okunev culture.[6]
In southern Siberia and Kazakhstan, the Andronovo culture was succeeded by the Karasuk culture (1500–800 BC). On its western border, it is roughly contemporaneous with the Srubna culture, which partly derives from the Abashevo culture. The earliest historical peoples associated with the area are the Cimmerians and Saka/Scythians, appearing in Assyrian records after the decline of the Alekseyevka culture, migrating into Ukraine from ca. the 9th century BC (see also Ukrainian stone stela), and across the Caucasus into Anatolia and Assyria in the late 8th century BC, and possibly also west into Europe as the Thracians (see Thraco-Cimmerian), and the Sigynnae, located by Herodotus beyond the Danube, north of the Thracians, and by Strabo near the Caspian Sea. Both Herodotus and Strabo identify them as Iranian.
2. Sintashta Culture (BC 2200-1900 BC)

Sintashta culture area
The Sintashta culture[a] is a Middle Bronze Age archaeological culture of the Southern Urals,[1] dated to the period c. 2200–1900 BCE.[2][3] It is the first phase of the Sintashta–Petrovka complex,[4] c. 2200–1750 BCE. The culture is named after the Sintashta archaeological site, in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, and spreads through Orenburg Oblast, Bashkortostan, and Northern Kazakhstan. The Sintashta culture is thought to represent an eastward migration of peoples from the Corded Ware culture.[5][6][7][8] It is widely regarded as the origin of the Indo-Iranian languages (Indo-Iranic languages[9][10]),[11][12][13] whose speakers originally referred to themselves as the Arya.[14][15]
The earliest known chariots have been found in Sintashta burials, and the culture is considered a strong candidate for the origin of the technology, which spread throughout the Old World and played an important role in ancient warfare.[16][17][18][19] Sintashta settlements are also remarkable for the intensity of copper mining and bronze metallurgy carried out there, which is unusual for a steppe culture.[20] Among the main features of the Sintashta culture are high levels of militarism and extensive fortified settlements, of which 23 are known.[21]
Origin[edit]
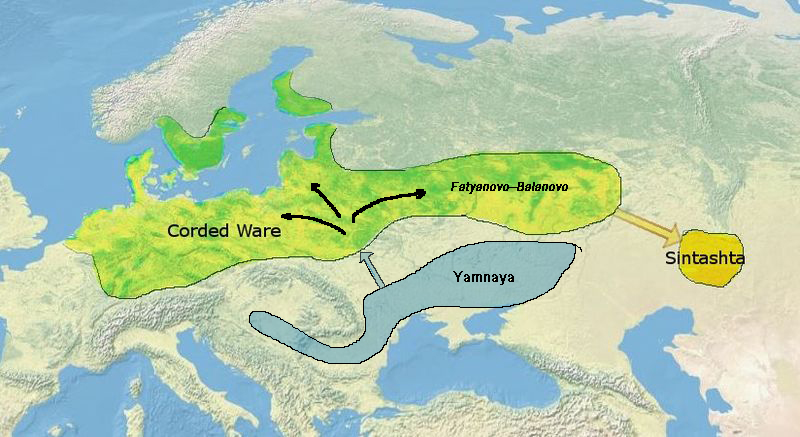
According to Allentoft et al. (2015), the Sintashta culture probably derived at least partially from the Corded Ware culture
Because of the difficulty of identifying the remains of Sintashta sites beneath those of later settlements, the culture was only distinguished in the 1990s from the Andronovo culture.[22] It was then recognised as a distinct entity, forming part of the "Andronovo horizon". Koryakova (1998) concluded from their archaeological findings that the Sintashta culture originated from the interaction of the two precursors Poltavka culture and Abashevo culture. Allentoft et al. (2015) concluded from their genetic results that the Sintashta culture should have emerged from an eastward migration of peoples from the Corded Ware culture.[23] In addition, Narasimshan et al. (2019) cautiously cite that "morphological data has been interpreted as suggesting that both Fedorovka and Alakul’ skeletons are similar to Sintashta groups, which in turn may reflect admixture of Neolithic forest HGs and steppe pastoralists, descendants of the Catacomb and Poltavka cultures".[24]
Sintashta emerged during a period of climatic change that saw the already arid Kazakh steppe region become even colder and drier. The marshy lowlands around the Ural and upper Tobol rivers, previously favoured as winter refuges, became increasingly important for survival.[citation needed] Under these pressures both Poltavka and Abashevo herders settled permanently in river valley strongholds, eschewing more defensible hill-top locations.[25]
Its immediate predecessor in the Ural-Tobol steppe was the Poltavka culture, an offshoot of the cattle-herding Yamnaya horizon that moved east into the region between 2800 and 2600 BCE. Several Sintashta towns were built over older Poltavka settlements or close to Poltavka cemeteries, and Poltavka motifs are common on Sintashta pottery.[26]
Sintashta material culture also shows the influence of the late Abashevo culture, derived from the Fatyanovo-Balanovo culture, a collection of Corded Ware settlements in the forest steppe zone north of the Sintashta region that were also predominantly pastoralist.....
Linguistic identity[edit]
Main articles: Proto-Indo-Iranic and Indo-Iranic peoples
See also: Indo-Iranic languages

Chariot model, Arkaim museum
Anthony (2007) assumes that probably the people of the Sintashta culture spoke "Common-Indo-Iranian". This identification is based primarily on similarities between sections of the Rig Veda, a religious text which includes ancient Indo-Iranian hymns recorded in Vedic Sanskrit, and the funerary rituals of the Sintashta culture as revealed by archaeology.[12] Some cultural similarities with Sintashta have also been found to be common with the Nordic Bronze Age of Scandinavia.[40]
There is linguistic evidence of interaction between Finno-Ugric and Indo-Iranian languages, showing influences from the Indo-Iranians into the Finno-Ugric culture.[41][42]
From the Sintashta culture the Indo-Iranian followed the migrations of the Indo-Iranians to Anatolia, the Iranian plateau and the Indian subcontintinent.[43][44] From the 9th century BCE onward, Iranian languages also migrated westward with the Scythians back to the Pontic steppe where the proto-Indo-Europeans came from.[44]
Warfare[edit]

Horses were domesticated on the Pontic-Caspian steppe[45]
The preceding Abashevo culture was already marked by endemic intertribal warfare;[46] intensified by ecological stress and competition for resources in the Sintashta period. This drove the construction of fortifications on an unprecedented scale and innovations in military technique such as the invention of the war chariot. Increased competition between tribal groups may also explain the extravagant sacrifices seen in Sintashta burials, as rivals sought to outdo one another in acts of conspicuous consumption analogous to the North American potlatch tradition.[25]
Sintashta artefact types such as spearheads, trilobed arrowheads, chisels, and large shaft-hole axes were taken east.[47] Many Sintashta graves are furnished with weapons, although the composite bow associated later with chariotry does not appear. Higher-status grave goods include chariots, as well as axes, mace-heads, spearheads, and cheek-pieces. Sintashta sites have produced finds of horn and bone, interpreted as furniture (grips, arrow rests, bow ends, string loops) of bows; there is no indication that the bending parts of these bows included anything other than wood.[48]
Arrowheads are also found, made of stone or bone rather than metal. These arrows are short, 50–70 cm long, and the bows themselves may have been correspondingly short.[48]
Sintashta culture, and the chariot, are also strongly associated with the ancestors of modern domestic horses, the DOM2 population. DOM2 horses originated from the Western Eurasia steppes, especially the lower Volga-Don, but not in Anatolia, during the late fourth and early third millennia BCE. Their genes may show selection for easier domestication and stronger backs.[49]
Metal production[edit]
|
External videos
|
|
|
The Sintashta culture - earliest chariots, fortified settlements and bronze metallurgy. Ivan Semyan
|
The Sintashta economy came to revolve around copper metallurgy. Copper ores from nearby mines (such as Vorovskaya Yama) were taken to Sintashta settlements to be processed into copper and arsenical bronze. This occurred on an industrial scale: all the excavated buildings at the Sintashta sites of Sintashta, Arkaim and Ust'e contained the remains of smelting ovens and slag.[25] Around 10% of graves, mostly adult male, contained artifacts related to bronze metallurgy (molds, ceramic nozzles, ore and slag remains, metal bars and drops). However, these metal-production related grave goods rarely co-occur with higher-status grave goods. This likely means that those who engaged in metal production were not at the top of the social-hierarchy, even though being buried at a cemetery evidences some sort of higher status.[50]
Much of Sintashta metal was destined for export to the cities of the Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) in Central Asia. The metal trade between Sintashta and the BMAC for the first time connected the steppe region to the ancient urban civilisations of the Near East: the empires and city-states of modern Iran and Mesopotamia provided a large market for metals. These trade routes later became the vehicle through which horses, chariots and ultimately Indo-Iranian-speaking people entered the Near East from the steppe.[51][52]
(source : Sintashta culture, wikipedia, 인용출처 : 본 블로그,)

3. Srubnaya culture (BC 1900-BC 1200)
 |
|
|
Geographical range
|
Pontic steppe
|
|
Period
|
Bronze Age
|
|
Dates
|
ca. 1900 BC – 1200 BC
|
|
Preceded by
|
Abashevo culture, Multi-cordoned ware culture, Sintashta culture, Lola culture
|
|
Followed by
|
Noua-Sabatinovka culture, Trzciniec culture, Belozerka culture, Bondarikha culture, Sauromatians
|
The Srubnaya culture (Russian: Срубная культура, romanized: Srubnaya kul'tura, Ukrainian: Зрубна культура, romanized: Zrubna kul'tura), also known as Timber-grave culture, was a Late Bronze Age 1900–1200 BC culture[1][2][3] in the eastern part of the Pontic–Caspian steppe. It is a successor of the Yamna culture, the Catacomb culture and the Poltavka culture. It is co-ordinate and probably closely related to the Andronovo culture, its eastern neighbor.[3] Whether the Srubnaya culture originated in the east, west, or was a local development, is disputed among archaeologists.[3]
The Srubnaya culture is generally associated with archaic Iranian-speakers.[3][4] The name comes from Russian сруб (srub), "timber framework", from the way graves were constructed.
Distribution[edit]

Chariot model, Arkaim museum

Srubnaya blades
The Srubnaya culture occupied the area along and above the north shore of the Black Sea from the Dnieper eastwards along the northern base of the Caucasus to the area abutting the north shore of the Caspian Sea, west of the Ural Mountains.[3] Historical testimony indicate that the Srubnaya culture was succeeded by the Scythians.[3]
Characteristics[edit]
The Srubnaya culture is named for its use of timber constructions within its burial pits. Its cemeteries consisted of five to ten kurgans. Burials included the skulls and forelegs of animals and ritual hearths. Stone cists were occasionally employed.[3] Srubnaya settlements consisted of semi-subterranean and two-roomed houses. The presence of bronze sickles, grinding stones, domestic cattle, sheep and pigs indicate that the Srubnaya engaged in both agriculture and stockbreeding.[3]
The use of chariots in the Srubnaya culture is indicated by finds of studded antler cheek-pieces (for controlling chariot horses), burials of paired domesticated horses, and ceramic vessels with images of two-wheeled vehicles on them.[5][6] The predecessor of the Srubnaya culture, a variant of the Abashevo culture known as the Pokrovka type, is considered to be an important part of the early ‘chariot horizon’, representing the rapid spread of the 'chariot complex'.[7][8]
Language[edit]
The Srubnaya culture is generally considered to have been Iranian.[3][4] Its area, which coincides with the presence of Iranian hydronyms,[4] has been suggested as a staging region from which the Iranian peoples migrated across the Caucasus into the Iranian Plateau.[3]
Genetics[edit]
See also: Fatyanovo-Balanovo culture § Genetics, Sintashta culture § Genetics, and Andronovo culture § Genetics

Admixture proportions of Srubnaya populations. They combined Eastern Hunter Gatherer ( EHG), Caucasian Hunter-Gatherer ( CHG), Anatolian Neolithic ( ) and Western Hunter Gatherer ( WHG) ancestry.[9]
Mathieson et al. (2015)[10] surveyed 14 individuals of the Srubnaya culture. Six men from 5 different cemeteries belonged to the Y-chromosome haplogroup R1a1. Extractions of mtDNA from fourteen individuals were determined to represent five samples of haplogroup H, four samples of haplogroup U5, two samples of T1, one sample of T2, one sample of K1b, one of J2b and one of I1a.
A 2017 genetic study published in Scientific Reports found that the Scythians shared similar mitochondrial lineages with the Srubnaya culture. The authors of the study suggested that the Srubnaya culture was ancestral to the Scythians.[11]
In 2018, a genetic study of the earlier Srubnaya culture, and later peoples of the Scythian cultures, including the Cimmerians, Scythians, Sarmatians, was published in Science Advances. Six males from two sites ascribed to the Srubnaya culture were analysed, and were all found to possess haplogroup R1a1a1. Cimmerian, Sarmatian and Scythian males were however found have mostly haplogroup R1b1a1a2, although one Sarmatian male carried haplogroup R1a1a1. The authors of the study suggested that rather than being ancestral to the Scythians, the Srubnaya shared with them a common origin from the earlier Yamnaya culture.[12]
In a genetic study published in Science in 2018, the remains of twelve individuals ascribed to the Srubnaya culture was analyzed. Of the six samples of Y-DNA extracted, three belonged to R1a1a1b2 or subclades of it, one belonged to R1, one belonged to R1a1, and one belonged to R1a1a. With regards to mtDNA, five samples belonged to subclades of U, five belonged to subclades of H, and two belonged to subclades of T. People of the Srubnaya culture were found to be closely related to people of the Corded Ware culture, the Sintashta culture, Potapovka culture and the Andronovo culture.[a][b] These were found to harbor mixed ancestry from the Yamnaya culture and peoples of the Central European Middle Neolithic.[13] The genetic data suggested that these cultures were ultimately derived of a remigration of Central European peoples with steppe ancestry back into the steppe.[c]
In a 2023 study, one sample from the site Nepluyevsky, belonging to Srubnaya-Alakul culture and located in Southern Urals, (c. 1877 to 1642 calBC), (2-sigma, 95.4%), featured Y-haplogroup R1a1a1b2a (R1a-Z94), and other not dated sample featured R1a1a1b2 (R1a-Z93).[14]
Gallery[edit]
- Ceramic sherd

- Bronze axes

- Horse bridle items

- Reconstructed Srubnaya hut

- Timber grave and tumulus
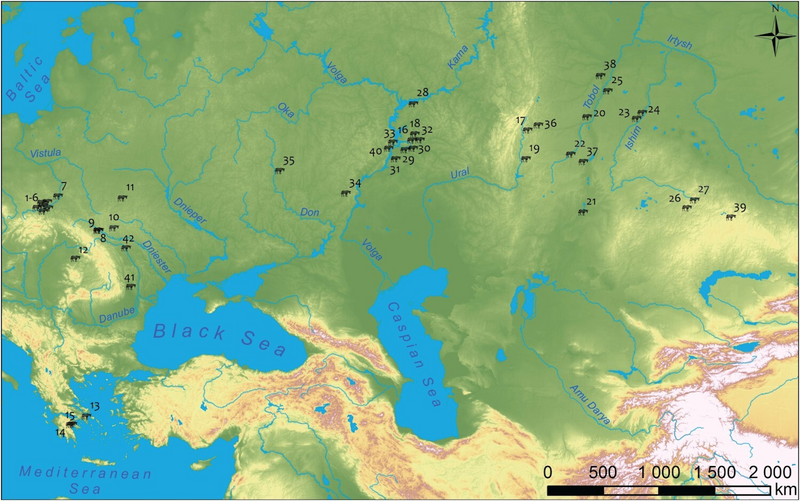
- Dispersion of double-horse burials ca. 2000-1400/1300 BCE.[15] Horses were domesticated on the Pontic-Caspian steppe.[16]

- Forensic reconstruction of a young woman (20-25), from the Aksay I cemetery, kurgan 9, burial 6, Late Bronze Age, Srubnaya culture.[17]
Notes[edit]
- ^ "We observed a main cluster of Sintashta individuals that was similar to Srubnaya, Potapovka, and Andronovo in being well modeled as a mixture of Yamnaya-related and Anatolian Neolithic (European agriculturalist-related) ancestry."[13]
- ^ "Genetic analysis indicates that the individuals in our study classified as falling within the Andronovo complex are genetically similar to the main clusters of Potapovka, Sintashta, and Srubnaya in being well modeled as a mixture of Yamnaya-related and early European agriculturalist-related or Anatolian agriculturalist-related ancestry."[13]
- ^ "Corded Ware, Srubnaya, Petrovka, Sintashta and Andronovo complexes, all of which harbored a mixture of Steppe_EMBA ancestry and ancestry from European Middle Neolithic agriculturalists (Europe_MN). This is consistent with previous findings showing that following westward movement of eastern European populations and mixture with local European agriculturalists, there was an eastward reflux back beyond the Urals."[13]
'Scythians Saka' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 스키타인에 대한 자료(3):스키타인 문화 (0) | 2024.05.10 |
|---|---|
| BC 2000년경 중앙아시아, 흑해위의 Saka 선조 문명에 대한 자료 (0) | 2024.04.14 |
| <펌>Scythians - wikipedia (0) | 2024.04.10 |
| 스키타인에 대한 자료 (0) | 2024.02.20 |
| <펌>Scythian religion (0) | 2020.09.12 |